Acute Pancreatitis: Etiology signs and Symptoms pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment
: / drgbhanuprakash
: https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr
: https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Acute Pancreatitis: Etiology , signs and Symptoms, pathophysiology , Diagnosis, Treatment
Overview:
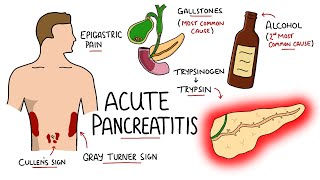
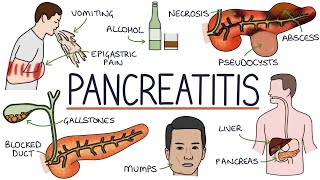
Acute pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition of the pancreas commonly caused by gallstones and alcohol use. It presents with sudden, severe epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric tenderness. Diagnosis is confirmed by elevated serum lipase or amylase levels and characteristic imaging findings on contrastenhanced CT abdomen. Severity and prognosis can be assessed using clinical scoring systems such as Ranson criteria and APACHE II.
Clinical Manifestations:
Epigastric pain: Sudden, severe pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back.
Nausea and vomiting: Common symptoms accompanying the abdominal pain.
Epigastric tenderness: Tenderness on palpation of the abdomen, typically in the epigastric region.
Diagnosis:
Laboratory tests:
Elevated serum lipase or amylase levels ≥ 3× the upper limit of normal (ULN).
Other laboratory abnormalities may include elevated liver function tests and inflammatory markers.
Imaging:
Contrastenhanced CT abdomen: Characteristic findings of acute pancreatitis include pancreatic enlargement, peripancreatic fat stranding, and fluid collections.
Management:
Supportive care:
Fluid resuscitation: Intravenous fluids to maintain adequate hydration and restore intravascular volume.
Analgesia: Pain management with appropriate medications, such as opioids.
Antiemetics: Medications to relieve nausea and vomiting.
Early enteral nutrition: Initiation of oral or enteral feeding as tolerated to support nutritional needs.
Identification and management of underlying cause:
Biliary pancreatitis: Cholecystectomy to remove gallstones or treat underlying biliary pathology.
Hypertriglyceridemiainduced pancreatitis: Longterm lipidlowering therapy to prevent recurrence.
Complications:
Localized complications:
Necrosis (necrotizing pancreatitis): Areas of pancreatic tissue death, which can become infected.
Pancreatic pseudocysts: Fluidfilled collections that develop in or around the pancreas.
Walledoff necrosis: Encapsulated areas of necrotic pancreatic tissue.
Systemic complications:
Sepsis: Infection spreading from the pancreas to other parts of the body.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Severe lung injury causing respiratory failure.
Organ failure: Dysfunction or failure of multiple organ systems.
Shock: Lifethreatening condition characterized by insufficient blood flow to organs.
Complications of acute pancreatitis are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Prompt diagnosis, appropriate management, and close monitoring are essential to minimize complications and improve outcomes.
#acutepancreatitis #pancreatitis #acutepancreatitispathology #acutepancreatitisusmle #acutepancreatitisosmosis #acutepancreatitisneetpg #acutepancreatitismbbs #mbbs #usmle #usmlestep1 #usmlestep2ck #usmlevideos #usmlelectures #medicalanimations #medicalvideos #medicalstudents #mbbsvideos #drgbhanuprakash #neetpg #fmge #neetpg #medicalcollege #medicalstudents #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #usmlestep1