Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition that affects the brain. It is the most common type of dementia.
Dementia is a term that refers to a loss of memory, language, problemsolving, and other thinking abilities that is severe enough to affect our daily life.
Alzheimer's disease is responsible for almost two out of every three cases of dementia. People with age 65 and above have 10 percent chances of developing Alzheimer's disease, while the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease increases with increasing age, For Example: risk of developing Alzheimer's disease at Age 85 is 35 percent.
In the brain, there are 100 billion nerve cells known as neurons. Each neuron cell communicates with many others neurons via synapse, forming a communication networks.
The brain tissue of an Alzheimer's patient has fewer and fewer nerve cells and connections. Two abnormal structures called plaques and tangles are the prime suspects in damaging and killing the nerve cells.
The plaques are aggregates of betaamyloid, an insoluble peptide that is cleaved from the extracellular portion of amyloid precursor protein (in short APP). APP is a large membrane protein that normally plays an essential role in neural growth and repair. When APP lose its function it is cleaved by two enzymes alpha and gamma secretase and the components of protein get dissolved. However, for unknown reasons, beta secretase enzyme might occasionally appear and cleave the APP. As a result, BetaAmyloid is produced, which cannot be dissolved, and sticks to other betaamyloid molecules, forming plaque outside the neurons. These plaques cause blockage between synapse and disrupt celltocell communication.
Beside this betaAmyloid plaque also stimulate immune response that appear to trigger the death of surrounding neurons. Which cause shrinkage of brain tissues.
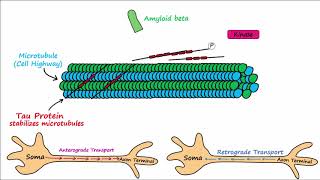
The other major component of Alzheimer’s pathology is Neurofibrillary Tangles (NFTs), which are composed of hyper phosphorylated tau protein.
The tau protein is generally involved in the formation and maintenance of microtubules. Microtubules are tubelike structures that help in the transportation of nutrients and other substances within the neuron. Due to the presence of Tau protein microtubules don’t break and held together tightly.
In Alzheimer’s disease, betaAmyloid plaque initiate pathways inside the neurons that activates kinase enzyme, which attach phosphate group to tau protein. This causes Tau protein to detach from microtubules and attach to itself, causing neurofibrillary tangles to develop. As a result Microtubules disintegrate, the cell shape changes, and the transport mechanism is interrupted.
Now let’s talk about the Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive disease, which means that symptoms get worse over time.
So we can categorize Alzheimer’s disease into Mild, moderate and severe.
Mild Alzheimer’s disease
It is the first stage of Alzheimer’s disease in which People develop memory problems and cognitive difficulties. It can last up to two to four years. Symptoms may include
• Forgetting simple things like keys and names
• Taking longer than usual to perform daily tasks
• Difficulty handling money or paying the bills
• Wandering and getting lost
• Experiencing personality and behavior changes, such as getting upset or angry more easily, and hiding things, etc.
Moderate Alzheimer’s disease
It is the second stage of Alzheimer’s Disease in which the parts of the brain responsible for language, senses, reasoning, and consciousness are damaged. It can last up to 2 to 10 years. Symptoms may include
• Greater memory loss and confusion
• Difficulty recognizing friends or family
• An inability to learn new things
• Difficulty performing tasks with several stages, such as getting dressed
• And hallucinations.
Severe Alzheimer’s disease
It is the late stage of Alzheimer’s disease in which plaques and tangles are present throughout the brain, causing the brain tissue to shrink substantially. It can last up to 1 to 3 years. This can lead to:
• An inability to communicate
• Dependency on others for care
• Being unable to leave the bed all or most of the time
• And finally, they lose their ability to swallow food and breathe, resulting in death.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but drugs and other treatments can help slow or ease the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral symptoms and improve the person’s quality of life.