Amino Acids - What Are And What Do Amino Acids Do - What Are Complete And Incomplete Proteins
In this video I discuss what are amino acids, what are amino acids made of, and what do amino acids do in the body. I also cover what are peptide bonds, polypeptide chains, how amino acids form proteins, some functions of amino acids, and what are amino acids used to build.
Transcript
We are going to start by looking at the molecular structure of a typical amino acid, don’t worry, I am going to make it easy to understand. The basic structure of amino acids is that they consist of a carboxyl group, a lone hydrogen atom, an amino group, and a side chain, which is often referred to as an Rgroup. The formation of the side chain is what makes amino acids different from one another.
As you can see in this diagram, these 4 are all connected to a carbon atom, which is referred to as the alpha carbon. Not every amino acid follows this exact structure, but, most do.
On the screen I have 3 different amino acids, lysine, tryptophan, and leucine. You can see that each has a carboxyl group, an alpha carbon, a amino group, and an Rgroup that is different from each other.
There are 23 total amino acids that are proteinogenic. Proteinogenic amino acids are precursors to proteins, which means they are compounds that participate in a chemical reaction to produce another compound.
Of these 23 amino acids, 20 of them are called standard amino acids, and the other 3 are nonstandard amino acids. These are listed on the screen. In this video we are going to focus on the standard amino acids, as they are what make up proteins.
These amino acids can be classified many different ways, we are going to classify them in a basic nutritional way. Essential and nonessential. Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body, so, they must come from foods we eat.
Nonessential amino acids are amino acids that our bodies can produce even if we don’t get them from the food we eat. There is a subgroup of nonessential amino acids that are considered to be conditional amino acids. The list of conditional amino acids is not definitive.
For instance, in times of illness or stress, there are certain amino acids the body cant produce sufficiently, and children's bodys haven’t developed the ability to produce certain amino acids yet.
There are 9 essential and 11 nonessential amino acids, ive listed them on the screen.
So, how do amino acids form proteins?
Proteins are built from the 20 standard amino acids.
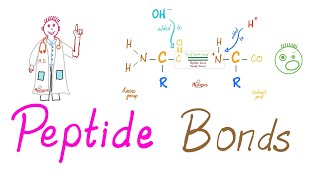
Well, the first thing that happens is that 2 amino acids come together to form a peptide bond. A peptide bond is when the carboxyl group of one amino acid bonds with the amino group of another amino acid, as you can see here.
If you notice 2 hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom have been removed from the peptide bonding process. So, the peptide bonding results in the release of a water molecule…h20.
But, we are not finished. More amino acids can link in, and form what is called a polypeptide chain. Some proteins are single polypeptide chains, and other proteins have polypeptide chains linked together. Not all protein contains all 20 of the standard amino acids.
Not all protein contains all 20 of the standard amino acids. Proteins are often labeled as complete or incomplete protein. A Complete protein is a protein source that contains a sufficient quantity of all 9 of the essential amino acids that we discussed earlier. An incomplete protein does not contain a sufficient quantity of all 9 of the essential amino acids.
Complete protein foods include…animal foods such as red meat, poultry, pork and fish. Eggs and dairy products such as cows milk, yogurt, and cheese. Plant foods such as soy products, black beans, kidney beans, pumpkin seeds, quinoa, pistachios, just to name a few. You can also combine incomplete protein foods to create a complete protein meal.
Amino acids also make up most enzymes. These Enzymes are proteins, so they are made by linking amino acids together in a specific and unique order. This chain of amino acids then forms a unique shape that allows the enzyme created to serve a single specific purpose. Enzymes function as catalysts, which means that they speed up the rate at which metabolic processed and reactions occur.
Amino acids can also be metabolized for energy. Some hormones like epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, are amino acid derived. Some neurotransmitters like serotonin are derived from amino acids. The amino acid arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide, which helps regulate blood pressure, improves sleep quality and increases endurance and strength.
Glutathione, which is a powerful antioxidant is formed from amino acids.
0:00 Intro
0:17 Basic molecular structure of amino acids
1:05 Proteinogenic amino acids
1:21 What are the standard amino acids?
1:38 What are essential and nonessential amino acids
1:59 How do amino acids form proteins?
2:49 What are complete and incomplete proteins?
3:35 Other functions of amino acids in the body