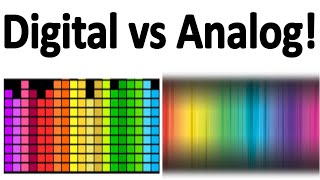
ANALOG COMPUTER || CHARACTERISTICS || ADVANTAGES || DISADVANTAGES || EXAMPLES
#ComputerGyan #Binarybytes #Computerknowledge
used Laptop used HP core i3 8GB 256GB SSD
An analog computer is a type of computing device you that processes data using continuous signals or physical quantities to represent and manipulate information. Unlike digital computers, which use discrete binary values (0s and 1s), analog computers use analog signals such as voltage, current, or physical phenomena like fluid pressure, mechanical rotations, or sound waves to perform calculations. Here's a description of analog computers:
Continuous Signals: Analog computers work with continuously varying signals, which can represent realworld phenomena with high precision. These signals can take any value within a given range, making them suitable for modeling and solving continuous mathematical equations.
Components: Analog computers consist of various analog electronic components, such as operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and inductors. These components are interconnected to create circuits that perform mathematical operations.
Applications: Analog computers were historically used for a wide range of applications, including engineering simulations, scientific research, control systems, and mathematical modeling. They were particularly useful for solving differential equations, which describe many physical processes.
Accuracy and Precision: Analog computers can provide high levels of accuracy and precision when modeling continuous systems. They excel at tasks that involve complex differential equations or the simulation of physical phenomena, such as electrical circuits, fluid dynamics, and mechanical systems.
Speed: Analog computers are often faster than digital computers for specific tasks, especially those involving continuous mathematical operations. They can solve differential equations in realtime or nearrealtime, which is crucial for applications like control systems.
Limited Versatility: One limitation of analog computers is their limited versatility. They are designed for specific tasks and are not programmable in the same way as digital computers. To perform a different computation, you often need to reconfigure the hardware.
Decline in Use: With the advent of digital computing technology, the use of analog computers has declined significantly. Digital computers offer greater flexibility, programmability, and the ability to handle discrete data and symbolic information, making them more suitable for a wide range of applications.
Examples: Historical examples of analog computers include the Differential Analyzer, an electromechanical device developed in the 1930s, and the electronic analog computer used for simulations in the mid20th century. Today, specialized analog computing techniques are still used in some niche applications, such as certain control systems and signal processing tasks.
In summary, analog computers are devices that process information using continuous signals and analog components. While they have historically been important for certain types of calculations and simulations, their use has become limited due to the widespread adoption of digital computers, which offer greater versatility and programmability.