Anatomy Of The Sartorius Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the anatomy of the Sartorius muscle.
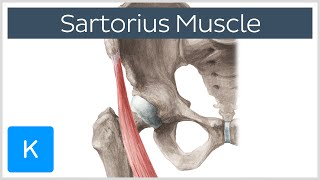
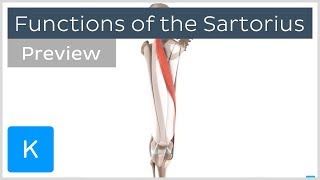
The Sartorius Muscle arises from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) of the pelvic bone. The Sartorius Muscle crosses the upper third of the thigh obliquely downwards medially and then descends vertically toward its insertion. It is a superficial muscle, the longest muscle and its fibers are parallel.
Insertion: The Sartorius Muscle is inserted into the anteromedial surface of the upper tibia. Other tendons are into the same location. These tendons are called the Pes Anserine tendons. Surgical approach to the Pes Anserine insertion for harvest of the semitendinosis and gracilis tendons puts the terminal branch of the saphenous nerve at risk as it emerges between the Sartorius and the gracilis tendons.
Innervation: the Sartorius muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve.
Function: The Sartorius Muscle flexes, abducts and rotates the hip laterally as well as flexes the knee. It is sometimes referred to as the “tailor’s muscle” in reference to the crosslegged position in which tailors once sat. The “Tailor” position helps to understand the function of the Sartorius muscle.
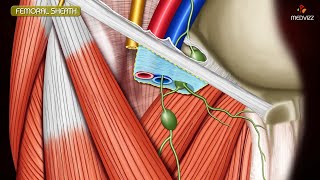
Anatomical & surgical considerations: the upper third of the Sartorius muscle forms the lateral border of the femoral triangle and its middle third forms the roof of the adductor (subsartorial) canal which contains the femoral vessels and the saphenous nerve. The femoral triangle is a superficial triangular space located on the anterior aspect of the thigh just inferior to the inguinal ligament.
The boundaries of the femoral triangle include:
1Lateral border: formed by the medial border of the Sartorius Muscle.
2Medial border: formed by the medial border of the adductor longus muscle.
3Bas: formed by the inguinal ligament
The femoral triangle contains three important structures: from lateral to medial:
1Femoral nerve
2Femoral artery
3Femoral vein
And it contains deep inguinal lymph nodes.
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh: crosses the lateral corner of the riangle, supplies the skin on the lateral part of the thigh. It appears that the neurovascular bundle is medial to the Sartorius muscle. Therefore, in the anterior approach to the hip, it is always safe to go lateral to The Sartorius Muscle in order to avoid the important structures within the femoral triangle. It is important to remember when performing this approach to avoid injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
Hip anterior approach (SmithPetersen): the intervenous plane superficially between the Sartorius (Supplied by the femoral nerve) and the tensor fascia lata (supplied by the superior gluteal nerve).
Bony avulsion of the Sartorius tendon occurs from a strong sudden pull of the Sartorius with the hip in extension and the knee in flexion. Avulsion of the Sartorius from its attachment sire most commonly occurs in sprinters and other running athletes. The avulsion can also occur after anterior iliac crest bone graft. It is advisable to start harvesting bone graft approximately 3 cm from the anterior superior iliac spine to avoid weakening of the bone and avulsion fracture. Harvesting bone within 3 cm of the ASIS may cause an avulsion fracture. Persistant hip pain after anterior iliac crest bone graft, get an Xray.
The adductor canal (subsartorial canal) is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh, extending from the apex of the femoral triangle to the opening of the adductor magnus, the adductor hiatus. The canal contains the femoral artery, femoral vein, and the saphenous nerve, which is a branch of the femoral nerve. It is important to recognize the relationship of the saphenous nerve to the Sartorius muscle and tendon. The saphenous nerve is posterior to the Sartorius tendon. Pes Anserine bursa is a small fluid filled sac located between the tibia and the three tendons of the Sartorius gracilis, and the semitendinosus. The pes anserine is the common area of insertion for the three tendons along the proximal medial aspect of the tibia.
Innervation of the pes anserine muscles:
Sartorius: femoral nerve
Gracilis: obturator nerve
Semitendinosus: tibial branch of the sciatic nerve.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundati...
Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library.
Song Title: Every Step