Anatomy Of The Tibialis Anterior Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the anatomy of tibialis anterior muscle.
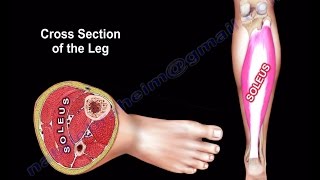
The leg has four muscle compartments. Each muscle compartment has a nerve. The tibialis anterior muscle is located within the anterior compartment of the leg.
Anterior compartment
Nerves within the compartment: deep peroneal nerve (numbness in the first webspace)
Muscles within the compartments: tibialis anterior, extensor halluces longus, extensor digitorum longus.
Tibialis anterior originates from the upper half and the lateral condyle of the tibia. It inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. The tibialis anterior muscle comes from the lateral surface of the tibia and at the ankle, it is the most medial structure. The tendon of the tibialis anterior along with the other extensor tendons pass under the extensor retinaculum. Here is a mnemonic phrase that can be used to remember the order of the artery, the nerve, and the tendons at the anterior ankle (anterior compartment). The T, h, v , n ,d and p of Tom has very nice dog and pig corresponds to Tibialis anterior, flexor halluces longus, Vessel (artery), Nerve, extensor Digitorum longus and Peroneus tertius.
Innervation: deep peroneal nerve L4 is more than L5. Remember the tibialis anterior muscle is more L4 than L5.
Interruption of the nerve supply:
•Pelvic fracture affecting L4L5 root.
•Posterolateral disc herniation – L3L4.
•Foraminal disc herniation L4L5.
Sciatic nerve injury: common peroneal nerve or deep peroneal nerve injury around the neck of the fibula. It is important to differentiate between common peroneal nerve that is high at the sciatic nerve and common peroneal nerve injury that is at the knee. Test the short head of the biceps femoris muscle.
Function of the tibialis anterior: forward flexion of the ankle and it also inverts the hindfoot. The tibialis anterior dorsiflexes the foot in preparation for heel strike during the late swing phase of the gate and it eccentrically contracts after the heel strike to slow progression to foot flat.
Rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon is an uncommon disorder that may cause loss of ankle dorsiflexion strength. Rupture may occur due to laceration. May also be a closed rupture. Closed rupture occurs due to strong eccentric contracture in young patients or attenuation rupture in the elderly who have diabetes, inflammatory arthritis or from steroid injections.
Presentation: difficulty clearing the foot during the gait with chronic rupture. In acute rupture, you will hear a “pop” and there will be swelling of the anterior ankle. Symptoms include: foot drop, steppage gait, pseudo tumor, anterior ankle pain, weak dorsiflexion, no tendon is felt in resisted dorsiflexion.
MRI will show that the tendon is missing.
Treatment: if partial tear use a cast. If complete tear AFO in low demand patients, however surgical repair proves to be successful in elderly patients. Surgery is the best choice. Acute repair, end to end repair when the tendon is normal. When there is chronic rupture, do autograft or an allograft attached to distal stump or midfoot. In patients with CVA and TBI, the tibialis anterior is constantly active, requiring surgical treatment. The procedure is split tibialis anterior tendon transfer combined with Achilles tendon lengthening or gastrocnemius recession. The tibialis anterior strength should be grade 4 or better.
The varus deformity in these patients is caused by over pull of the tibialis anterior or tibialis posterior muscles. EMG can establish which muscle is responsible.
Other important points: when foot drop occurs in compartment syndrome, it is due to involvement of the tibialis anterior and it usually indicates a late finding.
The tibialis anterior muscle and the peroneus longus muscle are antagonists.
In CharcotMarieTooth disease (peroneal muscle atrophy) the affected muscles become weak: tibialis anterior, peroneus brevis, intrinsic muscles of the hand and foot. The weak tibialis anterior muscle is overpowered by the unaffected peroneus longus muscle, bringing the first ray into a plantar flexed position.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundati...
Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library.
Song Title: Every Step