Antiarrhythmic Drugs
This is a brief overview of antiarrhythmic agents, or drugs used to resolve abnormal cardiac rhythms.
I created this presentation with Google Slides.
Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor.
ADDITIONAL TAGS
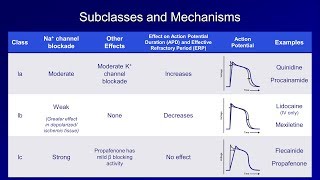
Class IA antiarrhythmic agent
Moderate sodium s, which s action potential duration
Quinidine
side effects blocks hERG , which results long QT and can cause torsades de pointes
Procainamide
Less prolongation QT segment, less TdP
Disopyramide
s force contraction heart
Side effects: constipation, urinary retention, glaucoma
IB antiarrhythmic
Mild sodium s, which s action potential duration
Lidocaine
Intravenous only
Mexiletine
Can be administered orally
IC antiarrhythmic
Marked sodium s, doesn’t change action potential duration
Flecainide
Possibly produces an ventricular arrhythmias
Propafenone
Some beta er effects (bradycardia and cardiac inotropy)
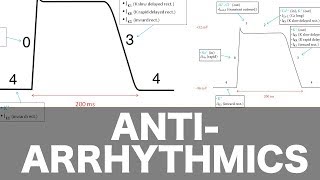
addition to changing AP duration by changing Na influx, Is also:
phase 4 depolarization
threshold potential
sub
degree Na+
AP duration change
Betaadrenergic receptor ers (beta ers)
catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine)
Reduces myocardial need for oxygen, can ischemia
slope phase 4 depolarization s selfgenerated rhythmic firing heart (s automaticity)
Prolong repolarization AV node → reentry
Effectively s refractory period
III antiarrhythmic
s potassium s (delayedrectifier potassium (DRK) s)
Prolongs repolarization (phase 3)
Amiodarone, Sotalol, Ibutilide, D etilide, Dronedarone
III: Amiodarone
Wide range effects through many mechanisms
s sinus node firing
s automaticity
s reentrant circuits
s Na, K, and Ca s ( I, III, IV antiarrhythmics)
s alpha and beta ( II) adrenergic receptors → vasodilation and d intropy
Treats many tachyarrhythmias: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, vtach, ventricular flutter, SVT
Pharmacokinetically unique: absorbed slowly, deposits adipose tissue
Half life 2560 days → cannot easily diminish or reverse effects
Side effects: pulmonary (pneumonia, pul fibrosis); cardiac (brady, arrhythmias, long QT, TdP); thyroid (due to iodine); GI; CNS
Amiodarone
Wide range effects through many mechanisms
sinus node firing; s automaticity; s reentrant circuits; Na, K, and Ca alpha and beta adrenergic receptors vasodilation and intropy
Treats many tachyarrhythmias: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, vtach, ventricular flutter, SVT
Pharmacokinetically unique: absorbed slowly, deposits adipose tissue
Half life 2560 days
Side effects: pulmonary (pneumonia, pul fibrosis); cardiac (brady, arrhythmias, long QT, TdP); thyroid (due to iodine); GI; CNS
High rates torsades de pointes
Dronedarone (amiodarone analog without iodine)
Gastrointestinal side effects but not TdP
Sotalol
Calcium Ltype Ca2+
Most effective cells dependant on Ca (SA, AV nodes)
transmission through AV node (for rapid atrial pulses)
Terminates reentrant rhythms
Treats AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (primary treatment)
Side effects: hypotension and heart failure pts taking betaers
Diltiazem and Verapamil
Digoxin
Inhibits activity sodium potassium pump (Na+K+ ATPase inhibitor)
Treats heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation (by decreasing heart rate)
s vagal tone; reduces sympa tic activity
Opens potassium (K+ activator)
Intravenously with saline flush (short 10 s half life)
Hyperpolarizes cells
Allows for rapid termination reentrant supraventricular tachycardia
chemical defibrillator

















![Antiarrhythmic Drug Class Mnemonic and Pharmacology [Made Easy Medical, Nursing, and USMLE]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gM9ic0zGttU/mqdefault.jpg)