Anti-diabetic medications
This is a short video on medications used to treat diabetes mellitus by lowering blood glucose levels
I created this presentation with Google Slides.
Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Insulin
Bind insulin receptor, activate tyrosine kinase receptor pathway
All used for DM1, DM2, GDM
Rapid acting insulin: Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine
Monomeric insulin analogs → monomers in solution
Peak time in 1 hour → no LAG
Used for postprandial glucose control
Short acting insulin: regular insulin
Same insulin found in human body → dimer/hexamer in sol’n
Peak in 2 to 4 hours
Administered IV for DKA
Intermediate acting insulin: NPH
Peak in 4 to 10 hours
Long acting insulin: glargine, detemir
Insulin analog → precipitates at body pH
Doesn’t really peak, relatively flat
Good for mimicking basal insulin secretion
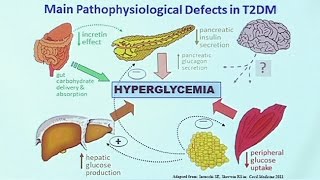
Biguanides
METFORMIN
Sensitizes to insulin
Thought to stimulate liver enzyme AMPK → exact MoA unclear
Does not require functioning beta cells
More effective in liver than muscle
Administered orally
Decreases HbA1c by 12%
Mild weight loss
SEs: diarrhea, nausea, vit B12 deficiency, lactic acidosis
Contraindicated in kidney/liver/heart failure
First line for DM2
Insulin
Thiazolidinediones
TZDs or glitazones: pioglitazone and rosiglitazone
Sensitizes to insulin → increases number and sensitivity
Bind to peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor gamma (PPARγ)
More effective in periphery (muscle/fat) than liver
Does not require functional beta cells
Administered orally
Decreases HbA1c by 11.5%
Mild weight gain, increases LDL, expensive, slow onset
SEs: weight gain, edema, heart failure, liver toxicity, fractures
Safe with renal failure
Increases secretion of insulin
Decreases HbA1c by 12%
SEs: weight gain, hypoglycemia, allergies (sulfa drugs)
Administered orally
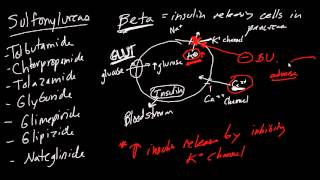
Sulfonylureas: tolbutamide, chlorpropamide, glipizide, glyburide, glimepiride
Binds to SU on the ATPactivated potassium of beta cells → requires functional beta cells
Blocks K channel → Ca influx → activate insulin release
Meglitinides: repaglinide, nateglinide
Bind to another receptor to block K channel → Ca influx → activate insulin release
Faster onset, slower duration, more expensive than sulfonylureas
Anti alpha glucosidase
Acarbose, miglitol
Slows absorption of carbohydrates in the proximal gut
Alpha glucosidase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes carbs in the brush border of the GI tract
Delays carb breakdown and thus absorption
Decreases postprandial hyperglycemia
Administered orally
Decreases HbA1c by 0.51%
SEs: flatulence (causes poor adherence), other GI disturbance, liver enzyme elevation
Expensive
Incretin mimetics
Incretins GLP1 and GIP are gutderived hormones that:
(1) stimulate insulin secretion, (2) inhibit glucagon secretion, (3) slow gastric emptying, and (4) promote satiety
Incretin release stimulated by eating
GLP1 receptor analogs: exenatide, liraglutide, dulaglutide
Mimick GLP1 and produce same incretin effects
Cause weight loss
Dipeptidyl peptidase4 (DPP4) is the enzyme that breaks down incretins
DPP4 inhibitors increase blood conc of incretins
agliptins: sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin
Administered orally
Amylin analogues
Synthetic amylin analogue: pramlintide
Cosecreted with insulin, deficient in diabetes, and has the following effects:
(1) inhibit glucagon secretion, (2) slow gastric emptying, (3) promote satiety
Decreases HbA1c by 0.51%
SEs: nausea, hypoglycemia
Promotes moderate weight loss
Administered orally or subcutaneously
Cause weight loss
Glycosurics
Promote renal excretion of glucose
Sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) is a channel in the proximal tubule responsible for 90% of glucose reabsorption
SGLT2 inhibitors: canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin
Decreases HbA1c by 0.51%
SEs: UTIs, vuvlvovaginal candidiasis (vaginal yeast infxns), glycosurea, renal failure, decrease blood pressure, hyperkalemia, dehydration
Promotes substantial weight loss
Colesevelam
Bile acid sequestrant → exact MoA unknown
Decreases HbA1c by 0.30.4%
SEs: constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, hypertriglyceridemia
Bromocriptine
Dopamine agonist → exact MoA unknown
Decreases HbA1c by 0.40.5%
SEs: headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting


















![TYPE 2 DIABETES: NEW NICE GUIDELINES [2022] EXPLAINED](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SlzcRoNWJd0/mqdefault.jpg)








