Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density (PSD) Examples in Digital Communications
Two fundamental examples in digital communication systems are used to explain Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density (PSD).
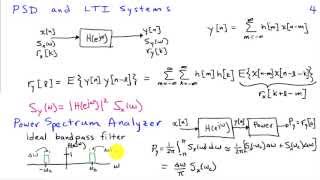
* Note that there is a small "typo" in the magnitude of the sinc function PSD that's drawn under the triangle function. The magnitude at f=0 should be (A^2)T. The triangle autocorrelation function can be viewed as the convolution of two identical rectangular functions of base T and height A/sqrt(T). The Fourier transform of that rectangular function is a sinc function with a height A sqrt(T). And since convolution in the time domain is equivalent to multiplication in the frequency domain, the Fourier transform of the triangle function will be a sinc^2 function with height (A^2)T.
** And here's an additional description that might also help with understanding the content in this video (based on a question I received in the comments under the video):
It's important to think about which random variable the expectation (ie. E[.]) is over. In this case the random variable is t_o. For some values of t_o the times t and t+tau will be within the same digital symbol period (and the value will be A*A). For other values, the times t and t+tau will be in different symbol periods (ie. the digital clock transition occurs between those two times). In this case the value will be either A*A, or (A)*A, or A*(A), or (A)*(A), with equal probability and the average of these will be 0. So overall, the average of the first case (A^2) and the second case (0) will depend on the percentage of the realisations of t_o that are in each case. The bigger the value of tau, the smaller the chance of t and t+tau being in the same digital period. Hence the Autocorrelation function goes down as tau goes up.
* If you would like to support me to make these videos, you can join the Channel Membership, by hitting the "Join" button below the video, and making a contribution to support the cost of a coffee a month. It would be very much appreciated.
Check out my search for signals in everyday life, by following my social media feeds:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?...
Instagram: / iainexplains
Related videos: (see http://www.iaincollings.com )
• What is Autocorrelation? • What is Autocorrelation?
• What is Power Spectral Density (PSD)? • What is Power Spectral Density (PSD)?
• Fourier Transform Duality Rect and Sinc Functions • Fourier Transform Duality Rect and Si...
• What is a Random Process? • What is a Random Process?
• What is a Poisson Process? • What is a Poisson Process?
• What does Wide Sense Stationary (WSS) mean? • What does Wide Sense Stationary (WSS)...
• What is a Probability Density Function (pdf)? • What is a Probability Density Functio...
• What is a Multivariate Probability Density Function (PDF)? • What is a Multivariate Probability De...
• Expectation Equation Explained • Expectation of a Random Variable Equa...
• What is White Gaussian Noise (WGN)? • What is White Gaussian Noise (WGN)?
• Duality Example in Fourier Transforms • Duality Example of Fourier Transforms
Full categorised list of videos and PDF summary sheets: http://iaincollings.com