Avascular Necrosis Osteonecrosis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes avascular necrosis and osteonecrosis.
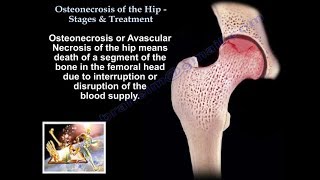
Avascular necrosis or osteonecrosis is death of a segment of bone due to loss of blood supply. Both bone cells and the bone marrow are affected. AVN I a common cause of hip pain in young and middle aged patients between 3550 years of age. It occurs more in males. AVN leads to severe degenerative arthritis of the hip joint and accounts for 10% of total hip replacement cases in the United States. The femoral head the most common site of atraumatic AVN. The humeral head is the second most common area. Bilateral AVN occurs in 80% of cases and each side may present a different stage. Check the other hip xrays even if asymptomatic.
The exact etiology and process of AVN is not known. Interruption of the blood supply of the femoral head is a common pathway. Genetic factors may also be implicated as the cause of AVN. Early diagnosis detects early stages of AVN that can be helped by a head preserving procedure such as decompression, bone graft or vascularized fibular graft. With multifocal osteonecrosis, three or more sites occur in about 3% of patients. It can affect the hip, knee, shoulder or ankle.
Patients with osteonecrosis at a different site than the hip should undergo an MRI of the hip to rule out asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the hip. Xrays are initially normal. MRI is the best study when the xray is normal and AVN is considered or suspected. The AVN is seen on the anterosuperior aspect of the femoral head. Trauma such as hip fracture or dislocation can cause AVN. The most common causes of AVN are steroid use, alcohol, gout, metabolic and genetic problems. The condition may be associated with a hypercoagulability state such as decrease in protein S, protein C, and factor V Leiden (We routinely get that study with AVN cases). The condition may also be idiopathic (without a cause), the AVN is a diagnosis of exclusion. If the Frog lateral view shows a crescent sign, it means that osteonecrosis is present and probably advanced. Double density on MRI is pathognomonic for AVN.
The patient may be asymptomatic and may present with dull hip pain (anterior groin pain) or severe arthritis pain due to collapse of the joint. With early arthritis, the patient will have a decrease in internal rotation of the hip. On the xray, the patient will have a flattened contour with collapse of the femoral head and decreased joint space.
If the joint surface is intact, without collapse, core decompression or vascularized bone graft is helpful. If the joint is collapsed, arthroplasty is the procedure of choice and rarely an osteotomy is done. Bisphosphonates are used in early stages of AVN. It prevents femoral head collapse, however, the results are controversial. Rule out other causes of hip pain such as gout, PVNS, femoral inguinal hernia, rheumatoid arthritis or stress fracture of the femoral neck.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundati...
Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library.
Song Title: Every Step