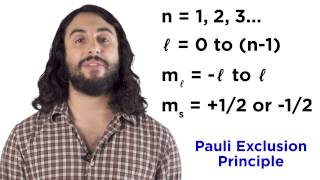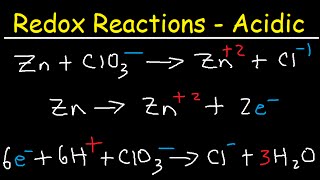Balancing Redox Reactions in Acidic and Basic Conditions
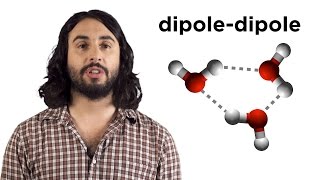
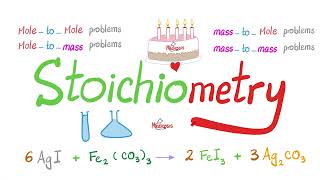
We know that redox reactions are ones that involve electron transfer. Something is oxidized, and something else is reduced. But these reactions can be tricky to balance when surrounding water molecules are involved in the reaction. Let's go through the algorithm for balancing redox reactions in both acidic and basic conditions.
Watch the whole General Chemistry playlist: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveGenChem
Study for the AP Chemistry exam with me: https://bit.ly/ProfDaveAPChem
Organic Chemistry Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveOrgChem
Biochemistry Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBiochem'>http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBiochem
Biology Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBio
Classical Physics Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDavePhysics1
Modern Physics Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDavePhysics2
Mathematics Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveMaths
EMAIL► [email protected]
PATREON► / professordaveexplains
Check out "Is This WiFi Organic?", my book on disarming pseudoscience!
Amazon: https://amzn.to/2HtNpVH
Bookshop: https://bit.ly/39cKADM
Barnes and Noble: https://bit.ly/3pUjmrn
Book Depository: http://bit.ly/3aOVDlT