Bragg’s law | Bragg's law derivation | Bragg's equation | Class XII | BSc | X-ray Diffraction | XRD
This video describes the Braggs law and also derives the mathematical statement of Braggs law
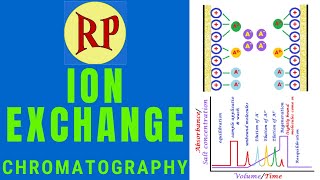
Bragg’s law states that when the Xray is incident onto a crystal surface, its angle of incidence(θ), will diffract with a same angle of diffraction/reflection/scattering, θ. For every diffracted beam, there exists a set crystal lattice planes such that the diffracted beam appears to be reflected from this set of planes.
For every diffracted beam, there exists a set crystal lattice planes such that the diffracted beam appears to be reflected from this set of planes.
Constructive interference occurs when the difference in path length is an integral multiple (n) of wavelength (l)
d – interlayer distance/distance between two layers/spacing of atomic planes in crystals
Theta– the angles of incidence at which these planes produce the most intense reflections (constructive interference)
lambda Wavelength of the incident beam
n – order of the diffraction/integer