BRAIN ANATOMY BASICS (In Rhyme!)
The central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord, yo
The brain’s in the neurocranium, the spinal cord’s below
Directions are: superior, inferior, dorsal, ventral,
Anterior posterior, lateral and medial, caudal and rostral
We examine the brain in sections: coronal and sagittal,
As well as the transverse, which is also called horizontal
The brain has five divisions that aid in localization,
And there are important structures at each and every station
The telencephalon, diencephalon, midbrain or mesencephalon,
Pons and cerebellum in the metencephalon, medulla in the myelencephalon
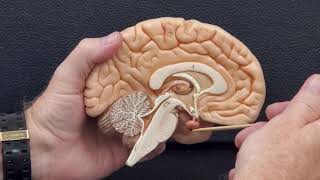
Next we will cover three key regions of the brain,
The brainstem, cerebellum, and cerebrum keep you sane
The brainstem includes the pons, medulla and midbrain,
These structures help involuntary responses sustain
The cerebellum helps you balance, and finetunes coordination
Its nickname is the “little brain”, which requires no explanation!
The cerebrum has 2 hemispheres, each with 4 lobes,
The hemispheres exchange signals with contralateral abodes
Note that the left hemisphere lets you understand language—
Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas give you this advantage!
The four lobes are the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital
Movement and problemsolving, are handled by the frontal
The occipital processes vision, the parietal handles touch
The temporal lobe does hearing, memory, language—oh so much!
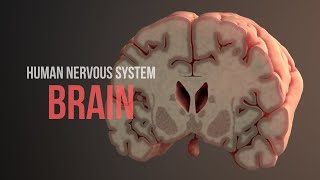
The outside of the brain is all wrinkled with convolutions:
Ridges called gyri and grooves called sulci, give surface area contributions
Deep furrows are called fissures Note the transverse and the lateral,
the central sulcus, and the largest one, the longitudinal
Besides the skull the brain has other strong protection,
With meninges as a barrier and with CSF shock absorption
The Dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater are meninges
The pia hugs the brain, while the dura’s on the fringes!
The cerebrospinal fluid, called the CSF for brief,
Provides the CNS with nutrients and cushioning relief!
It’s produced by choroid plexus in ventricles of the brain,
And absorbed in arachnoid granulations so that waste can drain
The falx cerebri is between the hemispheres where the dura dips,
Before the tentorium cerebelli, through the tentorial notch the brainstem slips
Four ventricles contain CSF – the 4th, the 3rd, and 2 lateral ones,
In between, through the cerebral aqueduct and intraventricular foramen the CSF runs!
Neurons are the unit of the brain, ah, back to the essentials!
The cell bodies decide whether the axons transmit action potentials
Axons form white matter, and are often myelinated, hey!
While cell bodies form grey matter, and messages relay
Three white matter tracts act as information relays:
Commissural, association, projection—the communication highways
Projection fibers go from the cortex to the brainstem and spinal cord,
Association fibers go within a hemisphere, bringing its regions into accord
The commissural fibers cross between the hemispheres;
The largest—the Corpus Callosum— links them without fears!
Also remember these structures: the insula, extreme capsule,
claustrum, external capsule, lentiform nucleus, and internal capsule
The neocortex is involved in higher order brain function,
Including your perception, spatial reasoning, and cognition
It has 6 layers, 16; the allocortex has 3 or 4—
It’s in the olfactory and hippocampal regions, so you can smell and remember more!
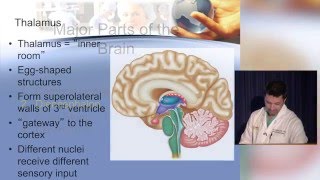
The thalami relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex,
Connected by the massa intermedia, it sorts a massive info vortex!
Superior and inferior colliculi sit at the brainstem’s back,
Without them, vision and eye movements would be out of whack!
The hypothalamus sets your body temp and releases hormones galore;
And contains the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which runs your circadian rhythm (snore)
The hypothalamus speaks to the pituitary gland,
Which then produces hormones on a scale very grand
The hippocampus consolidates shortterm memory to longterm,
The fornix is its major output tract, so keep that memory firm!
The fornix leads to the mammillary bodies, then the mammillothalamic tract,
So info arrives at the anterior thalamic nuclei intact
Then to the cingulate cortex, entorhinal cortex, and then hippocampus,
This is the Papez circuit; emotion and memory it helps grant us
The epithalamus connects the limbic system to other regions,
Inside is the pineal gland, for your melatonin secretions
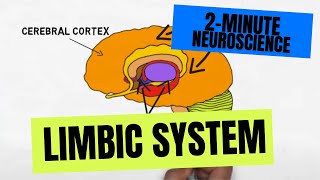
Straddling the thalamus, the limbic system brings emotions, like satisfaction,
Along with motivation, behaviour, long term memory and olfaction
It includes the amygdala, hippocampus, fornix, nucleus accumbens,
hypothalamus, mammillary bodies, as well as other friends
The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei,
Like the striatum, substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus—hi!
The striatum includes the putamen and globus pallidus of the lentiform nucleus
As well as the caudate, as you’ll remember if you are studious
Poetry advisor: Mara Lucien



![Lobes of the Brain: Cerebrum Anatomy and Function [Cerebral Cortex]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tZFW-waIpQg/mqdefault.jpg)