Cerebral Veins
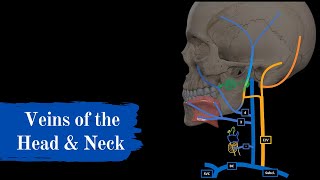
The venous drainage of the brain refers to the system of veins that collect deoxygenated blood and metabolic waste products from the brain tissue and transport them back to the heart for oxygenation. The venous drainage system of the brain is crucial for maintaining proper circulation and ensuring the removal of waste products. The primary veins involved in this system are the cerebral veins and the dural venous sinuses.
Here's an overview of the key components of the venous drainage of the brain:
1. Cerebral Veins: These are the veins that directly drain the brain tissue. They arise from the capillaries within the brain and converge to form larger veins. The cerebral veins are divided into two main groups: superficial cerebral veins and deep cerebral veins.
Superficial Cerebral Veins: These veins are located in the subarachnoid space (the space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater) on the surface of the brain. They collect blood from the cortex and superficial white matter and drain into the dural venous sinuses.
Deep Cerebral Veins: These veins are located within the brain substance. They collect blood from the deep white matter and basal ganglia. The deep cerebral veins typically drain into larger collecting veins that eventually empty into the dural venous sinuses.
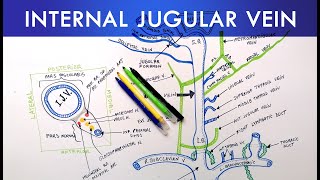
2. Dural Venous Sinuses: These are spaces located between the layers of the dura mater, the tough outermost membrane surrounding the brain. The dural venous sinuses are important channels for draining blood from the brain into the internal jugular veins, which ultimately return the blood to the heart. Some of the significant dural venous sinuses include:
Superior Sagittal Sinus: This is a large midline sinus located in the superior margin of the falx cerebri (a fold of the dura mater). It receives blood from the superior cerebral veins and eventually drains into the confluence of sinuses.
Transverse Sinuses: These sinuses are located on either side of the brain within the attached borders of the tentorium cerebelli (a fold of the dura mater). They receive blood from the confluence of sinuses and pass posteriorly to form the sigmoid sinuses.
Sigmoid Sinuses: These sinuses continue from the transverse sinuses and pass through the jugular foramina to become the internal jugular veins.
Confluence of Sinuses: This is the point where the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and occipital sinus meet. It serves as a common drainage point for several cerebral veins.
It's important to note that the brain's venous drainage system is interconnected and complex. Any disruption or blockage in this system can lead to problems such as increased intracranial pressure, venous congestion, and potentially serious medical conditions. Understanding the venous drainage of the brain is essential for neurosurgeons and healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat various neurological disorders.