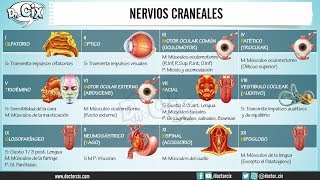
CN 4: Trochlear Nerve (Scheme Pathway Clinical Relevance) | Anatomy/Neurology
Content:
Introduction: 0:00
Trochlear Nerve Scheme: 00:52
Course of the Trochlear Nerve: 02:08
Functions of the Superior Oblique: 06:07
Trochlear Nerve Palsy: 07:55
Recap: 09:32
Channel membership: / @taimtalksmed
Follow my IG: / taimtalksmed
Donation link: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/taimtalk...
Trochlear Nerve Scheme / Overview:
Trochlea is Latin for ''Pulley'', due to the function of the superior oblique muscle
Nucleus of the trochlear nerve located in the midbrain, at the level of inferior colliculi
Emerges from the posterior surface of the midbrain, and turns anteriorly
Enter and run on the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus
Enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, to innervate the superior oblique
Exclusively a somatomotor nerve.
Course of the Trochlear Nerve:
Nucleus of the Trochlear nerve (nuclei nervi trochlearis) is located in the midbrain, at the level of the inferior colliculus (coliculi inferiores)
Nucleus is located at the same area as the oculomotor nerve nuclei, just a level lower.
The trochlear nerve crosses to the contralateral side, leaves from the posterior surface of the midbrain, and turns anteriorly.
Pierces the dura mater, and then runs through the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
Goes through the superior orbital fissure, to innervate the superior oblique.
Functions of the Superior Oblique Muscle:
Origin: Body of the sphenoid bone medial to the common tendinous ring.
Runs anteriorly, muscle tendon hooks around the trochlea of the superior oblique
Then takes a sharp posterior lateral turn
Insertion; Posterior Superolateral aspect of eyeball (deep to rectus superior, via trochlea orbitae)
Causes: Abduction, depression, internally rotation of the eyeball
Clinical Relevance:
Damage to the trochlear nerve can be caused by either congenital or acquired causes.
When the nerve is damaged, it causes the eye to naturally shift upwards and externally rotate leading to diplopia (double vision)
To compensate and reduce the diplopia, patients usually get a head tilt and chin tuck.
Congenital: Malformations of nucleus or nerve
Acquired: Trauma, or stroke in the midbrain.
Sources:
Singh, I. (2017). Human neuroanatomy (10th ed.). Helwany M, Bordoni B. Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 1 (Olfactory) [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan
Kozlowski, T. (2017). Memorix Anatomy: The Complete Study Guide. 2nd ed. Thieme Medical Publishers.
Pictures and visuals:
Complete Anatomy
Biorender
Powerpoint
Camtasia 2021