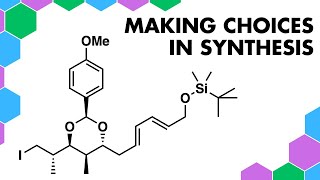
Elemental Metals in Retrosynthetic Analysis
A disconnection approach to a retrosynthesis of this organic molecule. The different ring systems can be made by classical named reactions involving metals in the forward synthesis.
The 1,4cyclohexadiene is clue for using a Birch reduction disconnection back to the benzene ring in the retrosynthesis. A mixture of sodium metal dissolved in liquid ammonia makes a solution of solvated electrons that act as a powerful reducing agent. Solvated electrons are transferred into the benzene pi system (pi cloud) to give a conjugated carbanion. This carbanion can be protonated by an external source of H+ such as an alcohol. The video includes a discussion of the reaction mechanism and the effect of both electronwithdrawing and electrondonating substituents on the regioselectivity for the Birch reduction.
The cyclopropane can be synthesised by SimmonsSmith reaction. The reagent for the SimmonsSmith cyclopropanation is a carbenoid formed by mixing zinc metal with diiodomethane. In this retrosynthetic analysis, the substrate for cyclopropanation is a chiral allylic alcohol. Due to restricted rotation, high levels of diastereoselectivity for cyclopropanation should be observed as the Z geometry of alkene next to the chiral centre leads to just one low energy conformation (energy minimum for this conformer). The SimmonsSmith zinc carbenoid reagent will coordinate to the hydroxyl group on the stereocentre and direct reaction to the same face.
The remainder of the retrosynthesis shows that the key intermediates can be made using simple disconnections and redox steps back to simple benzene ring systems. 1,2diX difunctional patterns are common here which can nudge towards the use of epoxides in a forward synthesis, although other synthetic pathways are possible.
#chemistry #organicchemistry #education