ENT Types of Tracheostomy Tracheotomy difference level High mid low Percutaneous dilatational Mini
Playlist • ENT 05 Larynx Trachea OtoRhinoLaryngo...
• Emergency tracheostomy
Airway obsturction
Urgent need to establish airway
Intubation or laryngotomy (cricothyrotomy) are either not possible or feasible
slash trach
See procedure next slide
• Elective or tranquil tracheostomy
Orderly or Routine Tracheostomy
Local/ General Anaesthesia
(a) Therapeutic, to relieve respiratory obstruction, remove
tracheobronchial secretions or give assisted ventilation.
(b) Prophylactic, to guard against anticipated respiratory
obstruction or aspiration of blood or pharyngeal secretions
such as in extensive surgery of tongue, floor
of mouth, mandibular resection or laryngofissure.
Usually temporary
• Permanent tracheostomy
Bilateral abductor paralysis
Laryngeal stenosis
• Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy
ICU
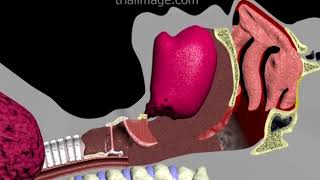
2 cm below the lower border of cricoid
Entry to trachea – b/w 2nd and 3rd ring
Flexible Bronchoscope to monitor needle, guide wire and dilator
• Mini tracheostomy / Laryngotomy(cricothyroidotomy) cricothyroidotomy
High – above the level of thyroid isthmus, violates the 1st ring of trachea. In Larynx carcinoma, in res. Obstruction ?, Tracheostomy at this site
can cause perichondritis of the cricoid cartilage and subglottic
stenosis and is always avoided
Mid
Low – below the level of isthmus, in resp insufficiency, Trachea is deep at this level and close to several large
vessels; also there are difficulties with tracheostomy tube which impinges on suprasternal notch.