Explained: Normal Shock Relations
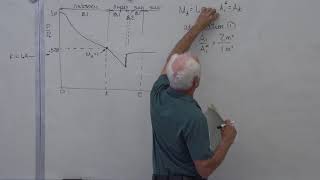
In this video we will go through the full derivation of the normal shock relations. We will solve for downstream Mach number (M2), velocity ratio (u2/u1), density ratio (rho2/rho1), pressure ratio (P2/P1), and temperature ratio (T2/T1). We will assume the gas is calorically perfect (i.e. the specific heats are constant), which allows us to solve for all these values as only a function of specific heat ratio (gamma) and the upstream Mach number (M1).
===== ERRORS =====
► For the board from 9:09 10:33, the terms in brackets on the top line are correct, but the terms in brackets on the next two lines are incorrect (I switched a negative sign with a positive sign). When I bring the expression over to the next board at 10:34, the bracketed term is back to being correct, with a negative sign instead of the positive sign. [Thank you Pratheesh Prabhakar]
► From 21:44 to the end of the video, the second bracketed term in the final T2/T1 equation should be inverted (i.e, I have written it there as rho2/rho1, where it should really be rho1/rho2 as mentioned on the line above). [Thank you Pratheesh Prabhakar and Osama Hamdy]
===== RELEVANT VIDEOS =====
→ 1D Mass Eqn
https://goo.gl/0vesye
→ 1D Momentum Eqn
https://goo.gl/FHFUi4
→ 1D Energy Eqn
https://goo.gl/RSXVyc
→ Thermally Perfect Gas
https://goo.gl/maElnm
→ Specific Heats
https://goo.gl/kdf1B7
→ Isentropic Relations
https://goo.gl/Q8Rv9O
===== REFERENCES =====
► Notes by Matt MacLean
► Modern Compressible Flow, Anderson
► Elements of Gasdynamics, Liepmann and Roshko
► Gas Dynamics, Zucrow and Hoffman









![The most beautiful equation in math, explained visually [Euler’s Formula]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/f8CXG7dS-D0/mqdefault.jpg)