Flexor Digitorum Superficialis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the anatomy of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle.
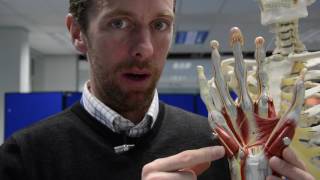
The flexor digitorum superficialis is a superficial digits flexor. The flexor digitorum superficialis covers the radius and the ulna. The FDS covers the flexor digitorum profundus.
The carpal tunnel area contains nine flexor tendons and four of them are for the FDS.
The FDS for the ring and middle fingers lies volar to the index and the small fingers. The FDS tendon of the fifth finger may not be present in all individuals.
Origin: the FDS arises from two heads; a humeroulnar head and a radial head. The humeroulnar head arises from the medial epicondyle (common flexor tendon oroigin, humeral part), and from the medial side of the coronoid process (ulnar part). The radial head arises from thje oblique upper third of the anterior border of the radius (anterior oblique line).
The muscle then divides into four tendons to the medial four fingers.
The FDS muscle separates and creates a tunnel for the FDP to go through. At the proximal third of the proximal phalanx, the FDS splits to pass around the FDP. The two slips of the FDS rotate 180 degrees around the FDP and then two slips reunite deep to the FDP in the region known as “camper’s chiasma”, dorsal to the FDP. Then they insert into the radial and ulnar aspect of the proximal half of the middle phalanx.
Insertion: the FDP inserts by four tendons into the base of the middle phalanges of fingers 25.
Action: the FDS flexes the middle phalanges at PIP and MCP joints of digits 25.
Innervation: median nerve (C7, C8. T1).
Relationship to the median nerve: after the median nerve passes between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle, it passes deep to the FDS muscle and it appears superficial approximately two inches from the wrist joint. In the proximal third of the forearm, the ulnar artery is located between the FDS and the FDP.
How do you test the flexor digitorum superficialis?
The patient will attempt to flex the involved finger at the PIP joint with or without resistance while remaining three fingers are held fully extended in order to eliminate the function of the flexor digitorum profundus. Check the integrity of the FDP tendon. The finger lies in slight extension relation to other fingers. The finger will have no active flexion of the DIP joint. you will extend all the joints of the finger except the DIP and then ask the patient to flex the DIP. If the patient can flex the DIP joint, then the FDP is intact.
Flexor tendon injury zones
Indication for reimplantation of a digit involves injury distal to the insertion of the FDS.
One of the contraindications to reimplantation of a digit is a single digit proximal to the FDS insertion.
Zone I
Distal to FDS insertion.
Zone II
Fibrosseous tunnel; A1 pulley to zone I.
Zone III
Carpal tunnel to A1 pulley.
Zone IV
Carpal tunnel.
Zone V
Proximal to carpal tunnel.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC














![Hand of Benediction vs the Claw Hand [feat. the Ulnar Paradox]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BWhB_B3e4gc/mqdefault.jpg)