Gluconeogenesis | Pathway Overview | Gluconeogenic precursor | Metabolism | Biochemistry Basics
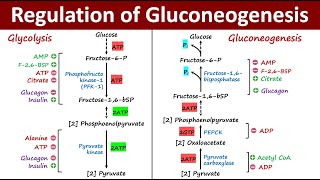
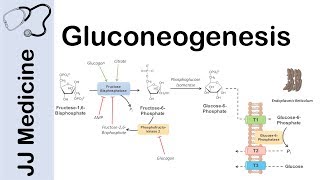
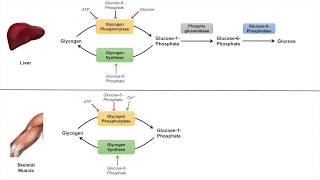
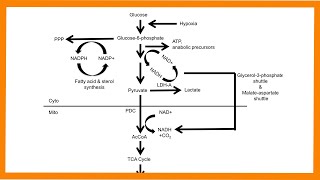
This video provides a tutorial on Pathway of Gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis means synthesis of new glucose from noncarbohydrate substrates. There are four important enzymes which bypass the irreversible reactions of glycolysis, this include, pyruvate carboxylase, PEPcarboxykinase, fructose 1,6bisphosphate and glucose 6phosphatase. Pyruvate is first carboxylated to oxaloacetate which requires ATP, biotin and pyruvate carboxylase enzyme. Subsequently, oxaloacetate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate. Through series of reactions, PEP is then converted to fructose 1,6bisphosphate. Fructose 1,6BSP is then converted to fructose 6phosphate via fructose 1,6bisphosphatase enzyme and finally glucose6phosphate is converted to glucose with the help of glucose 6phosphatase enzyme. Glucogenic precursors include lactate, glycerol, propionate and amino acids (except for leucine and lysine). Gluconeogenesis consumes 6 molecules of ATP.
The following topics are covered in this lesson,
1. What is gluconeogenesis?
2. Enzymes of gluconeogenesis
3. Pyruvate carboxylase
4. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
5. Fructose 1,6bisphosphatase
6. Glucose 6phosphatase
7. How is pyruvate converted to phosphoenolpyruvate?
8. How is free glucose generated from glucose?
9. Comparison of gluconeogenesis vs glycolysis
10. What are the precursors of gluconeogenesis
11. What are glucogenic amino acids?