Gross anatomy of Right atrium (RA) Animation | Usmle step 1 National exit test
: / drgbhanuprakash
: https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr
: https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Right atrium Content courtesy Dr Vishram singh
The right atrium (RA) is one of the four chambers of the human heart, and is the first chamber to receive deoxygenated blood returning from the body. It plays an important role in originating and regulating the conduction of the heart.
Gross anatomy
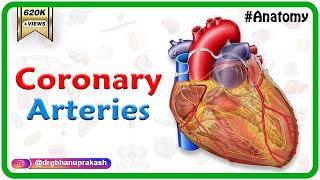
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava (SVC), the inferior vena cava (IVC), the coronary sinus (covered by the thebesian valve), and the thebesian veins.
It is grossly the shape of an irregular ellipsoid, with the exception of the right atrial appendage, which arises anteriorly. The right atrial appendage overlies the aortic root and the proximal right coronary artery (RCA).
normal size (measured at end systole on four chamber view)
no accepted standard reference measurements
enlargement usually determined qualitatively
RA volume not routinely measured on echocardiography
long axis: 3.45.3 cm
short axis: 2.64.4 cm
area: 1018 cm2
echocardiography measurement, tends to be larger on CT or MRI
The right atrium is separated from the left atrium by the interatrial septum. In cases of congenital cardiac malformations, the morphologic right atrium can be identified by the fossa ovalis in the interatrial septum.
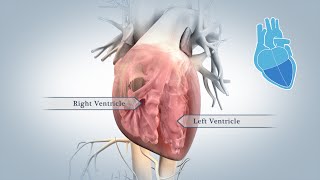
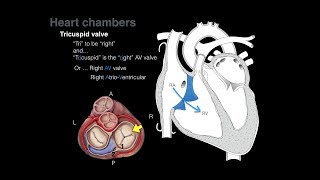
The right atrium leads into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
One of the main anatomic landmarks of the right atrium, the crista terminalis is a muscular ridge on the anterior aspect of the chamber. The atrium is lined by pectinate muscles to the left of this crest, and these extend into the right atrial appendage. The atrial lead of an external pacemaker is frequently located in these muscles. To the right of the crista terminalis, the atrial lining is smooth and this represents the right horn of the sinus venosus.
Blood supply
arterial supply is primarily from the right coronary artery (RCA) and several of it's branches:
conus artery (first branch off RCA in 55%, otherwise arises off left circumflex artery)
sinoatrial node artery (usually second branch off RCA in 60%)
acute marginal branches
venous drainage
variable veins drain the atrial wall
tiny myocardial thebesian veins drain directly into the right ventricle
Nerve supply
The right atrium is the location of the sinoatrial node, the heart's pacemaker. It is located subepicardially in the terminal groove, near the junction of the SVC and right atrium.
Although the sinoatrial node can generate conduction rhythms spontaneously, it is regulated by the vagus nerve (CN X) and the cardiac sympathetic plexus.
The atrioventricular node receives conduction impulses from the atrium and propagates it into the ventricular bundles. It is located between the coronary sinus ostium, the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve, and the tendon of Todaro (which connects the thebesian and Eustachian valves).
#rightatrium #heartanatomy #anatomyofrightatrium #usmlevideos #cardiologyvideos #cardiacanatomy #cardiology #atrium #grossanatomyatrium #rightatriumanatomy #usmlestep1 #mbbs #usmle #medicalstudents #fmge #usmleprep #medicalcollege #usmlestep1videos #neetpg