Heel Pain u0026 The Baxter's Nerve - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the condition of heel pain associated with the Baxter's nerve, the etiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Pain located at the heel of the foot has many causes. It is important to make a correct diagnosis of the cause of the heel pain so that appropriate treatment can be given to the patient.
Common causes of heel pain include:
1Baxter’s nerve compression
2Plantar fasciitis
3Fat pad atrophy
4Achilles tendonitis
5Stress fractures of the calcaneus.
6Lumbar spine radiculopathy.
The site and location from different causes of the pain appear to be close to each other. It is difficult to determine the source of the pain and this makes diagnosis difficult or confusing.
Plantar fasciitis: irritation and swelling of the thick tissue on the bottom of the foot. This fascia can become inflamed and painful, making walking more difficult. Plantar fasciitis is most severe in the morning when the patients first stand on their feet. Stretching exercises or walking often help in relieving the painful tightening associated with plantar fasciitis. Pain symptoms will intensify with prolonged exercise or standing. Plantar fasciitis is usually associated with a tight heel cord.
Fat pad atrophy: in fat pad atrophy the fat that cushions the calcaneus is thinned. This condition is common in elderly people and can cause significant pain while walking. History of steroid injection
Achilles tendonitis: chronic injury to the tendon that joins the heel to the muscles of the lower leg primarily occurring from overuse. Achilles tendon gives us the ability to rise up on our toes, allowing for the act of walking and Achilles tendonitis can make walking painful and difficult.
Stress fracture of the calcaneus can occur due to overuse injury. The patient will experience weight bearing pain. Stress fracture injuries of the hell are typical of running sports due to repetitive shock being placed on the heel. Side to side compression of the calcaneus is painful.
Lumbar spine radiculopathy: pain on the lateral side of the foot can result from L5S1 radiculopathy.
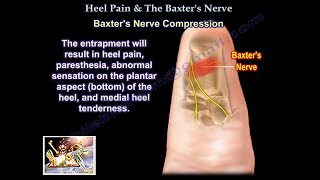
The Baxter's nerve is the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The Baxter's nerve contributes to 20% of all heel pain cases. The Baxter's nerve provides motor innervation to the abductor digiti minimi muscle.when the nerve is affected by compression, the symptoms appear to look like plantar fasciitis. Entrapment of Baxter's nerve may cause up to 20% of heel pain but it is still overlooked.
Course of the Baxter's nerve
The first branch of the lateral plantar nerve is the inferior calcaneal nerve ( Baxter’s nerve). The nerve courses vertically between the abductor halluces and the quadratus plantae muscles, then make a 90degree horizontal turn, coursing laterally beneath the calcaneus to innervate the abductor digiti minimi muscle.
The Baxter's nerve can become entrapped within the medial heel. The entrapment will result in heel pain, paresthesia, abnormal sensation on the plantar aspect (bottom) of the heel, and medial heel tenderness. Two sites of entrapment are typical with Baxter's nerve impingement:
1Between the fascia of the abductor hallucis and quadratus plantae muscles.
2Where the nerve passes along the anterior aspect of the medial calcaneal tuberosity.
Treatment: management is usually conservative.
•Heel stretching exercises
•Rest
•NSAIDS
•Orthotics
•Surgery is the last resort with neurolysis of the nerve after the release of the deep fascia of the abductor hallucis muscle. There is a good to excellent result in about 90% of patients after decompression of the nerve. Involvement of the baxter’s may affect running athletes casuing pain on the medial planatr aspect of the foot.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC




![BEST Heel Nerve Pain Treatment [Baxters Nerve Entrapment Treatment]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1ZqubXExmc4/mqdefault.jpg)

![Nerve Heel Pain SECRETS [Plantar Fasciitis vs. Baxter's Nerve]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jBXHBBM26kw/mqdefault.jpg)





![Burning, Tingling, Numbness in Feet & Legs [Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DoqjV9VR5tA/mqdefault.jpg)