Hip Dislocation Following Total Hip replacement - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Educational video describing the condition of hip dislocation after total hip surgery.
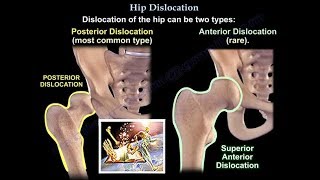
Types of hip dislocation:
1posterior
2anterior
The position of the leg is important in determining the type of hip dislocation. When the hip is dislocated, the leg is usually shortened and it assumes a different position than the normal leg ( the other leg).
If the dislocation is posterior, the leg will be in adduction and internal rotation. If the dislocation is anterior, the leg will be in abduction and external rotation. Notice that the affected extremity is shortened and externally rotated. Leg shortening can also be seen in hip fractures and the leg will be shortened and externally rotated.
Dislocation of the hip following total hip surgery may require revision surgery but it is rare. The majority of hip dislocations after total hip dislocations are posterior and they are usually treated without surgery. Most occur within the first month of THA. Incidence 14% in primary, 16% in revision. There is more incidence of dislocation in revision hip replacement.
Causes and risk factors
•Posterior approach: try to repair the capsule adequately
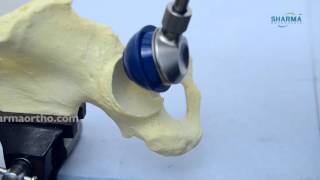
•Malposition of the compartment: ideally the normal cup component will be in 20 degrees of anteversion and 40 degrees of abduction. When the hip dislocated posterior, always check for retroversion of the cup.
•Prior hip fracture surgery especially in the elderly.
•Weakness of the abductor musclemust achieves soft tissue tension and function.
•Alcohol abuse
•Improper neck lengthlooseness of the hip.
Avoid activity that causes dislocation after total hip surgery.
Patient should use a pillow between the legs while sleeping on the back.
Do not cross the legs during sleep.
Do not bend the body at the waist past 90 degrees.
Do not bend over to tie your shoes. Do not sleep on the side.
Keep more than a 90 degrees angle while sitting.
Do not sit in a chair that makes it difficult to stand up.
Do not sit in a chair with legs crossed.
The patient should be aware that if the leg changed its usual position or became shortened, then the hip is probably dislocated. Consult your doctor.
xrays of the dislocated total hip should include AP and lateral views. Look for eccentric wear and look for the position of the prosthesis.
CT scan may be needed before or after reduction of the dislocation to check the version of the components.
Treatment is variable and depends on the situation. The treatment should be tailored to each case. The majority of these cases with early dislocations can be treated successfully with closed reduction and immobilization. The treatment should start with closed reduction of the total hip and immobilization. Hip stability is checked after reduction of the dislocation. Immobilization can be done by a brace or a hip spica.
Trochanteric osteotomy and advancement of the trochanter and tensioning the abductor's muscle. Screws or wires can be used. The prosthesis must be in good alignment for this procedure to work.
Constrained acetabular components are used when the abductor's muscle is deficient and the component position is good. Revision total hip is done in recurrent dislocation with malposition of the component or polyethylene wear.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC