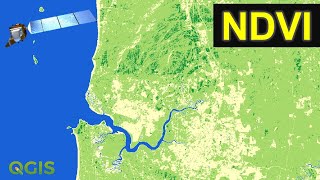
how to calculate NDVI using ArcGis
The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) is a standardized index allowing you to generate an image displaying greenness (relative biomass). This index takes advantage of the contrast of the characteristics of two bands from a multispectral raster dataset—the chlorophyll pigment absorptions in the red band and the high reflectivity of plant materials in the nearinfrared (NIR) band.
An NDVI is often used worldwide to monitor drought, monitor and predict agricultural production, assist in predicting hazardous fire zones, and map desert encroachment. The NDVI is preferred for global vegetation monitoring because it helps compensate for changing illumination conditions, surface slope, aspect, and other extraneous factors (Lillesand 2004).
The differential reflection in the red and infrared (IR) bands enables you to monitor density and intensity of green vegetation growth using the spectral reflectivity of solar radiation. Green leaves commonly show better reflection in the nearinfrared wavelength range than in visible wavelength ranges. When leaves are water stressed, diseased, or dead, they become more yellow and reflect significantly less in the nearinfrared range. Clouds, water, and snow show better reflection in the visible range than in the nearinfrared range, while the difference is almost zero for rock and bare soil. The NDVI process creates a singleband dataset that mainly represents greenery. The negative values represent clouds, water, and snow, and values near zero represent rock and bare soil.