Inferior Mesenteric Artery(IMA) | Abdominal Aorta Branch | Hindgut Blood Supply
The inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is a major branch of the abdominal aorta. It supplies arterial blood to the organs of the hindgut – the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon, splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum.
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the inferior mesenteric artery – its anatomical position, major branches and clinical correlations.
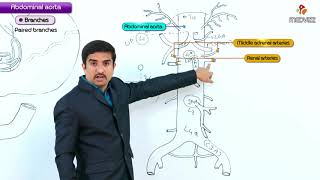
The inferior mesenteric artery is the last of the three major anterior branches of the abdominal aorta (the other two are the coeliac trunk and superior mesenteric artery). It arises at L3, near the inferior border of the duodenum, 34 cm above where the aorta bifurcates into the common iliac arteries.
As the artery arises from the aorta, it descends anteriorly to its parent vessel, before moving to the left side. It is a retroperitoneal structure – situated behind the peritoneum.
The branches of the inferior mesenteric artery supply the structures of the embryonic hindgut. These include the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon, splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum.
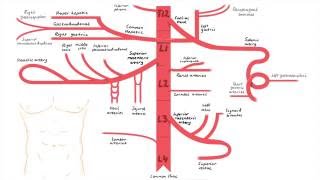
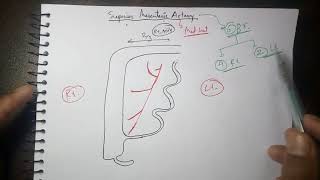
There are three major branches that arise from the IMA – the left colic artery, sigmoid artery and superior rectal artery.
Left Colic Artery
The left colic artery is the first branch of the IMA. It supplies the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon and the descending colon. After arising from its parent artery, it travels anteriorly to the psoas major muscle, left ureter and left internal spermatic vessels, before dividing into ascending and descending branches:
Ascending branch – crosses the left kidney anteriorly, before entering the mesentery of the transverse colon, moving superiorly. It supplies the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon, and the upper aspect of the descending colon.
Descending branch – moves inferiorly to supply the lower part of the descending colon. It anastomoses with the superior sigmoid artery.
Sigmoid Arteries
The sigmoid arteries supply the descending colon and the sigmoid colon. There are typically 24 branches, with the uppermost branch termed the superior sigmoid artery. They run inferiorly, obliquely and to the left, crossing over the psoas major, left ureter and left internal spermatic vessels.
Superior Rectal Artery
The superior rectal artery is a continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery, supplying the rectum. It descends into the pelvis, crossing the left common iliac artery and vein.
At the S3 vertebral level, the artery divides into two terminal branches – one supplying each side of the rectum. Within the walls of the rectum, smaller divisions of these branches eventually communicate with the middle and inferior rectal arteries.