Insulin Mechanism and Side Effects
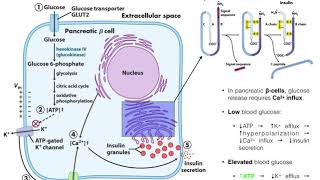
Insulin is a peptide hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels in the body. It is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, which are located in clusters known as the islets of Langerhans. Insulin helps control glucose metabolism by facilitating its uptake into cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for later use.
Here are some key points about insulin:
1. Glucose Regulation: When you consume carbohydrates, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. Elevated blood glucose levels trigger the release of insulin from the pancreas. Insulin enables glucose to enter various cells in the body, such as muscle, fat, and liver cells, where it can be used as a source of energy or stored as glycogen (a form of stored glucose).
2. Anabolic Hormone: Insulin is often referred to as an anabolic hormone because it promotes the synthesis of molecules, such as proteins and fats, and inhibits their breakdown. In muscle cells, insulin helps promote the uptake of amino acids for protein synthesis, aiding in muscle growth and repair.
3. Diabetes: Diabetes is a medical condition characterized by impaired insulin production or inadequate response to insulin. There are two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: In this autoimmune condition, the immune system attacks and destroys the insulinproducing beta cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or use of insulin pumps to manage their blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes: This is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin. Over time, the pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Type 2 diabetes is often managed through lifestyle changes, oral medications, and in some cases, insulin therapy.
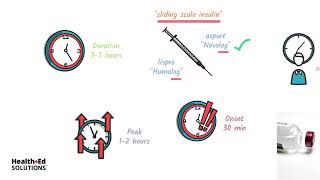
4. Insulin Administration: Insulin can be administered through injections using insulin pens, syringes, or insulin pumps. The method and frequency of administration depend on the type of diabetes and the individual's specific needs.
5. Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia: Insufficient insulin or inadequate response to insulin can lead to high blood sugar levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia. Conversely, taking too much insulin or not consuming enough carbohydrates can lead to low blood sugar levels, a condition called hypoglycemia. Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can have serious health consequences if not managed properly.
6. Research and Development: Research continues to advance our understanding of insulin's role in the body and how to improve its administration. There have been efforts to develop alternative insulin delivery methods, such as inhalable insulin, to make treatment more convenient for individuals with diabetes.
Insulin is a critical hormone that helps regulate energy metabolism and maintain stable blood sugar levels. Its discovery and subsequent development as a treatment for diabetes have had a significant impact on the lives of millions of people worldwide.