Kienbock's Disease - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes Kienbock's Disease. Lunate carpal bone avascular necrosis, the etiology, the signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and the treatment options.
Kienbock's Disease is avascular necrosis of the lunate. The lunate is one of many carpal bones of the hand and wrist. Avascular necrosis of the lunate bone usually occurs in males 2040 years of age. Usually the patient will have a negative ulnar variance, meaning the ulna is shorter, which increases the radiolunate contact stress.
What is negative ulnar variance? Normally the distribution of forces across the wrist is 80/20. Ulnar variance is load passing through the wrist. Positive ulnar variance: ulna 2.5 mm longer. Negative ulnar variance ulnar is 2.5 mm shorter.
How do you measure ulnar variance? Measure from the radial articular surface and the height of the ulnar head. Negative variance increases the shear forces on the lunate.
Lunate vascularity variances: X,Y and I pattern, with I pattern having the highest rick of avascular necrosis.
Kienbock's Disease may be caused be repetitive trauma. The blood supply of the lunate bone may become interrupted. Initially the condition feels like a wrist sprain, however if it is not recognized and detected early the condition will progress to collapse of the lunate and arthritis of the wrist.
Classification and concept of treatment
Stage I: Xrays normal, but changes are seen on MRI. Treatment is splint, NSAID medication, surgery is rare.
Stage II: sclerosis of the lunate the bone maintains shape. Treatment is one of three ways: 1 joint leveling procedure: in negative ulnar variance radial shortening osteotomy. In positive or neutral ulnar variance capitate shortening. 2 distal radius core decompression incites a local vascularization healing in the lunate. 3 revascularization procedure.
Stage IIIa: the lunate begins to collapse with no scaphoid rotationtreat as stage II.
Stage IIIa: the lunate has collapsed with fixed scaphoid rotation. Treatment is proximal row carpectomy (PRC) or STT fusion.
Stage IV: degenerated adjacent intercarpal joints. Treatment is total wrist arthrodesis, total wrist arthroplasty, proximal row carpectomy (PRC).
Presentation:
•Activity related
•Insidious onset
•More in dominant hand
•Decreased rom and stiffness
•Decreased grip strength.
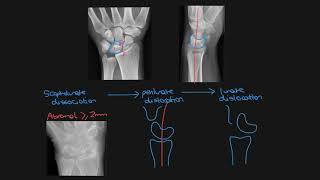
An easy way to recognize Kienbock's Disease is to look at the xray of the wrist. If the ulna is short, then check the lunate color. Whitish in color = Kienbock's Disease. The lunate is white and the ulna is short (negative ulnar variance), you usually need to shorten the radius, decompress the radius, or revascularize the lunate.
Get an MRI for early detection when there is negative ulnar variance and negative xray with wrist pain. CT scan is useful when collapse of the lunate occurs (CT scan shows the lunate necrosis and destruction of the trabeculae).
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundati...
Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library.
Song Title: Every Step








![How To Treat Nerve Pain in the Foot, Toes & Legs [Causes & Treatment]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/rr0sG8moSHQ/mqdefault.jpg)