Liver and its role in digestion
The liver is the largest solid organ and the largest gland in the human body. It carries out over 500 essential tasks.
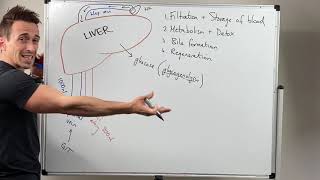
Classed as part of the digestive system, the roles of the liver include detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of chemicals that help digest food.
Fast facts on the liver
The liver is classed as a gland.
This vital organ carries out more than 500 roles in the human body.
It is the only organ that can regenerate.
The liver is the largest solid organ in the body.
Alcohol abuse is one of the major causes of liver problems in the industrialized world.
Structure
Weighing between 3.17 and 3.66 pounds (lb), or between 1.44 and 1.66 kilograms (kg), the liver is reddishbrown with a rubbery texture. It is situated above and to the left of the stomach and below the lungs.
The skin is the only organ heavier and larger than the liver.
The liver is roughly triangular and consists of two lobes: a larger right lobe and a smaller left lobe. The lobes are separated by the falciform ligament, a band of tissue that keeps it anchored to the diaphragm.
A layer of fibrous tissue called Glisson’s capsule covers the outside of the liver. This capsule is further covered by the peritoneum, a membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity.
This helps hold the liver in place and protects it from physical damage.
Functions
The liver is classed as a gland and associated with many functions. It is difficult to give a precise number, as the organ is still being explored, but it is thought that the liver carries out 500 distinct roles.
The major functions of the liver include:
Bile production: Bile helps the small intestine break down and absorb fats, cholesterol, and some vitamins. Bile consists of bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin, electrolytes, and water.
Absorbing and metabolizing bilirubin: Bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of hemoglobin. The iron released from hemoglobin is stored in the liver or bone marrow and used to make the next generation of blood cells.
Supporting blood clots: Vitamin K is necessary for the creation of certain coagulants that help clot the blood. Bile is essential for vitamin K absorption and is created in the liver. If the liver does not produce enough bile, clotting factors cannot be produced.
Fat metabolization: Bile breaks down fats and makes them easier to digest.
Metabolizing carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are stored in the liver, where they are broken down into glucose and siphoned into the bloodstream to maintain normal glucose levels. They are stored as glycogen and released whenever a quick burst of energy is needed.
Vitamin and mineral storage: The liver stores vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12. It keeps significant amounts of these vitamins stored. In some cases, several years’ worth of vitamins is held as a backup. The liver stores iron from hemoglobin in the form of ferritin, ready to make new red blood cells. The liver also stores and releases copper.
Helps metabolize proteins: Bile helps break down proteins for digestion.
#digestion
#Liverfunctions
#RoleoFLiverInDigestion