Metformin Mechanism and Side Effects
Metformin is a widely used oral medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as biguanides. It is primarily prescribed to treat type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production by the pancreas. Metformin is not used to treat type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn't produce insulin at all.
Here are some key points about Metformin:
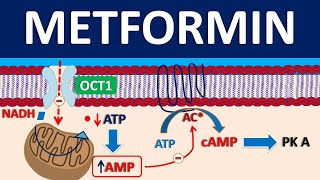
1. Mechanism of Action: Metformin works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and increasing the sensitivity of muscle cells to insulin. This helps the body use glucose more effectively, reducing the amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream.
2. Insulin Sensitivity: One of the main benefits of Metformin is its ability to enhance insulin sensitivity. It helps cells take up glucose from the blood more efficiently, thereby improving the body's response to insulin.
3. Glucose Production: Metformin reduces the liver's production of glucose. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, the liver often produces too much glucose, contributing to high blood sugar levels.
4. Weight Neutrality: Unlike some other diabetes medications that can lead to weight gain, Metformin is generally considered weightneutral or even associated with slight weight loss. This is beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes who may already struggle with weight management.
5. Side Effects: Common side effects of Metformin can include gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort. These side effects can be doserelated and may improve over time. Serious side effects are rare, but it's important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any unusual symptoms.
6. Lactic Acidosis: While rare, Metformin can potentially lead to a serious condition called lactic acidosis. This occurs when there's a buildup of lactic acid in the bloodstream. It's more likely to occur in individuals with kidney or liver problems. As a result, Metformin is generally not prescribed to people with severe kidney impairment.
7. Combination Therapy: Metformin is often prescribed as a firstline treatment for type 2 diabetes. It can be used alone or in combination with other oral medications or insulin to help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
8. Other Uses: Metformin has been investigated for its potential benefits beyond diabetes management. Some studies suggest that it might have a role in treating conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and even certain types of cancer. However, these uses are still being studied and are not yet established.
9. Dosage and Administration: The dosage of Metformin varies depending on the individual's needs, medical history, and response to the medication. It is usually taken with meals to minimize gastrointestinal side effects.
As with any medication, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting or making any changes to your treatment plan involving Metformin. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific medical history and needs.