Nerve Fibers Classification Part 2: Spinal Nerves and Cranial Nerves (1-6)
Spinal Nerves:
Spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord. Those emerging from the anterior or ventral side are motor nerves, primarily serving voluntary skeletal muscles. As they convey motor messages "away" from the CNS, they are termed "Efferent" nerves. These nerves are also "somatic," as they influence muscles derived from somites, and are considered "general" due to their widespread presence in the body. Collectively, these nerve fibers are categorized as "General Somatic Efferents."
Sensory fibers arise from the posterior or dorsal side of the spinal cord, serving the body wall, skin, tendons, and joints. These fibers handle sensations such as touch, pain, temperature, vibration, proprioception, and twopoint tactile discrimination, originating mainly from the somatopleura. These are similarly "general" and are referred to as "General Somatic Afferent"
The lateral gray column of the spinal cord also contributes fibers. From its ventral part, fibers serve visceral organs and are associated with the autonomic nervous system, classified as "general visceral efferent." Fibers from the dorsal part supply the viscera, managing sensory inputs such as distention.
Cranial Nerves:
Olfactory Nerve: This afferent nerve carries smell sensations from the nose to the brain. The classification of the olfactory mucosa as either visceral or somatic is debated, but generally, smell is considered a visceral sensation due to its chemical detection mechanism. Though the olfactory epithelium originates from the ectoderm, suggesting a somatic classification, the unique nature of smell leads to its categorization as either special visceral or somatic afferents.
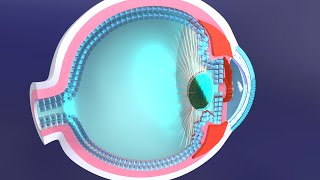
Optic Nerve: This nerve carries visual sensory information to the brain. As the eyes are not considered deeply seated visceral organs and are derived from neuroectoderm, the optic nerve fibers are classified as "special somatic afferents" due to the unique and exclusive nature of vision.
Oculomotor Nerve: This nerve supplies all the eye muscles except the lateral rectus and superior oblique. They are supplied by "General Somatic Efferent" nerve fibers, because eye muscles are derived from somites. It also include the "General Visceral Efferent" fibers for Sphincter Pupillae muscle.
Trochlear Nerve: It innervates the superior oblique muscle. Since these extrinsic eye muscles are derived from somites like skeletal muscles, the nerve fibers are "General Somatic Efferent."
Trigeminal Nerve: This nerve transmits sensory information such as touch, pain, and temperature from the head and neck, and is thus classified as "general somatic afferent." It also includes fibers termed "special branchiomotor efferents" or "Special Visceral Afferent" for muscles of mastication and the tensor tympani, which originate from the 1st pharyngeal arches.
Abducent Nerve: Like the trochlear nerve, it supplies the lateral rectus muscle with "General Somatic Efferent" fibers.