nerve injury of the upper and lower extremity complete easy review of nerve injuries
1 long thoracic nerve: medial winging of the scapula is most commonly caused by deficit in the serratus anterior muscle due to impingement of the long thoracic nerve.
2 Median nerve injury: carpal tunnel syndrome: inflammation of the carpal tunnel compresses the median nerve and causes tingling, numbness, weakness, or pain in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger. Surgical release of the carpal tunnel is needed.
3 Ulnar nerve injury: cubital tunnel syndrome: pressure on the nerve at the elbow can cause numbness or pain in the elbow, hand, wrist, or fingers. Compression of the ulnar nerve below the elbow may lead to claw hand.
4 Posterior interosseous nerve injury: at about the level of the lateral epicondyle, the radial nerve begins to divided into the deep branch and the superficial branch of the radial nerve. The posterior interosseous nerve (deep) enters the extensor compartment of the forearm through the supinator muscle. The posterior interosseous nerve supplies these muscles on the radial side and dorsal surface of the forearm. The posterior interosseous nerve does not supply cutaneous sensation and is purely a motor nerve. Entrapment at the Arcade of Frohse: with injury to the posterior interosseous nerve, the patient will experience difficulty with extension of the fingers only.
5 Anterior interosseous nerve injury: about half the way down the forearm, the anterior interosseous nerve exits from the dorsal lateral aspect of the median nerve. The anterior interosseous nerve is purely motor. All the muscles in front of the forearm are supplied by the median nerve except the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus. The anterior interosseous nerve gives branches to three muscles: Pronator quadratus, lateral half of the flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus. The patient will be unable to give the OK sign due to paralysis of the flexor pollicis longus and the flexor digitorum profundus.
6 Radial nerve injury: radial nerve compression or injury may occur at any point along the course of the nerve.
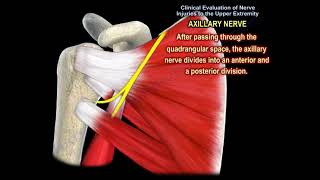
7 Axillary nerve injury: the axillary nerve supplies the deltoid muscles, giving sensation over the shoulder area. The axillary nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. When the nerve is injured: weakness of shoulder abduction, atrophy of the deltoid, numbness in the deltoid region. The axillary nerve is commonly injured due to fractures or dislocations of the shoulder joint.
8 Femoral nerve injury: the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh are innervated by the femoral nerve. The usual cause of femoral nerve dysfunction are due to trauma or compression of the nerve. The quadriceps tendon is a strong tendon which groups the four muscles that extend the knee: rectus femoris, vastus intermedius (under rectus femoris), vastus medialis, vastus laterlaris.
Differential diagnosis: tears of the quadriceps tendon, patellar tendon injury or patellar fractures cause an inability to extend the knee. A quadriceps tendon rupture is rupture of the tendon that inserts into the top of the patella.
9 Posterior tibial nerve injury: the tarsal tunnel is located just below the medial malleolus of the ankle and is covered with a thick band of ligaments called the flexor retinaculum. The flexor retinaculum protect the structures contained within the tunnel such as the posterior tibial nerve. The structures which also pass through the tunnel include the posterior tibial artery, the tendons of the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and the flexor hallucis longus. Tarsal tun el syndrome is a compression neuropathy caused by compression of the posterior tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel. With tarsal tunnel syndrome there will be pain and numbness on the plantar aspect of the foot and heel. Tibial nerve compression with tarsal tunnel syndrome is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome which occurs at the wrist.
10 Common peroneal nerve injury: the ankle and foot dorsiflexors are supplied by the peroneal nerve which is part of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve starts in the lower back and runs through the buttock and lower limb. In the lower thigh, just above the back of the knee, the sciatic nerve divides into two nerves, the tibial and the peroneal nerves, which innervate different parts of the lower leg. The common peroneal nerve then travels anterior, around the fibular neck, dividing into superficial and deep peroneal nerves. The deep peroneal nerve gives innervation to the tibialis anterior muscle of the lower leg which is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle. Conditions causing foot drop: injury to the knee: knee dislocation: in the event of knee dislocation, it is important to check for common peroneal nerve and popliteal artery injury.
Become a friend on facebook:
/ drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC














![The Brachial Plexus Animated Review [HD]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5YJJkK4Kw88/mqdefault.jpg)









