NMR spectroscopy in easy way - Part 2 || How it works?
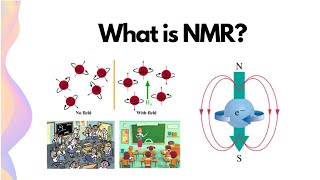
Learn easily how NMR spectroscopy works and what is the larmor frequency and how it is related with magnetic field strength. Nuclei with spin quantum number I as 1/2 can give the NMR signal and in presence of externally applied magnetic field they can show types of orientations. One is parallel to applied filed and another one is opposite to it. Nuclei can undergo transition from one state to another state by supplying radiowaves matching with frequency gap between these two states. This frequency is known as resonating or Larmor frequency.
In the part1 of this video, principle of NMR spectroscopy was discussed in detail. you can watch here. • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 1
Here we will see the effect of electronegativity on chemical shift of nuclei under study.
Part 2 : How NMR works : • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 2...
Part3 : NMR spectral interpretation and rules: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 3...
Part4 : NMR spectral table: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 4...
Part5 : Magnetic anisotropy: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 5...
Part6: Solvents in NMR : • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part6...
Part7: 1H vs 13C NMR : • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 7...
Part8: Number of NMR signals: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 8...
Part9: Magnetic equivalence: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 9...
Part10: NMR signals in cyclic compounds: • NMR spectroscopy in easy way Part 1...
#NMR
#Larmorfrequency
#ShieldingEffect



















![HNMR Spectroscopy Basics [Livestream Recording] Organic Chemistry Review & Practice Session](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/zpBsAY8K89s/mqdefault.jpg)







