Otic ganglion /Anatomy/ Secretomotor (parasympathetic and sympathetic) pathway of parotid gland
@SmartMedLearnDrAnkitJain #oticganglion #anatomyofoticganglion #oticganglionbranches #oticganglionanatomy #octicganglionfunction #anatomy #usmlestep1 #smartmedlearn
x
like , comment , share , subscribe
To Subscribe our youtube channel, click here
https://www.youtube.com/c/SmartMedLea...
Telegram group Anatomy knowledge (Smart Med Learn) link:
https://t.me/smartmedlearnsdrankitjain
Facebook page :
/ smartmedlearn
x
To watch more videos, please click here:
Playlist : Head and neck anatomy
• Head and Neck Anatomy
Playlist : Lower limb anatomy
• Lower Limb Anatomy
Playlist : Upper limb anatomy
• Upper Limb Anatomy
Playlist : Neuroanatomy
• Neuroanatomy
x
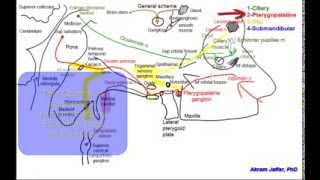
OTIC GANGLION
It is a small parasympathetic ganglion connected to the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve and provides a relay station to the secretomotor fibres to the parotid gland.
Topographically, it is intimately related to the mandibular nerve but functionally it is related to glossopharyngeal nerve.
Location
Infratemporal fossa, just below the foramen ovale.
Relations
Lateral: Mandibular nerve.
Medial: Tensor palati muscle.
Posterior: Middle meningeal artery.
Anterior: Medial pterygoid muscle.
Roots or Connections
1. Parasympathetic motor (secretomotor): From lesser petrosal nerve. Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres arise from inferior salivatory nucleus; pass successively through glossopharyngeal nerve, tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve (Jacobson’s nerve), tympanic plexus, and lesser petrosal nerve to relay in the ganglion. Postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from ganglion cells pass through auriculotemporal nerve to supply parotid gland.
2. Sympathetic: From sympathetic plexus around the middle meningeal artery. Preganglionic sympathetic fibres arise from T1 and T2 spinal segments, enter the cervical sympathetic chain at
the level of its inferior ganglion and then ascend to relay in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. The postganglionic fibres arise from this ganglion and form plexus around the middle meningeal artery. They then pass through the ganglion without relay to reach the parotid gland via auriculotemporal nerve. They are vasomotor in nature and responsible for thick salivary secretion.
3. Sensory: From auriculotemporal nerve.
4. Somatic motor: Nerve to medial pterygoid. It passes through ganglion to supply medial pterygoid, tensor palati, and tensor tympani muscles.
x
Thank you
Smart Med Learn
Dr. Ankit Jain
MBBS, MS




![Mandibular Nerve Course, branches and distribution |Trigeminal nerve| [Simplified]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/9UKgrOj_bVA/mqdefault.jpg)