Over 100% Assay Efficiency in qPCR? Not so fast. -- Ask TaqMan #21
Submit your question: http://bit.ly/1cgFftk
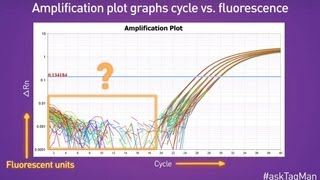
In another Ask TaqMan video, we discussed assay efficiency and how to calculate it. But how does efficiency really impact our experiments, or as Julie Kase at George Washington University asks, why is it important? Does the efficiency for all of my targets have to be the same? The aim for all assays is to be 100% efficient, which means there is an exact doubling of your template every cycle.
We previously found that this can be calculated thru a dilution series and the following equation. In order to use the ΔΔCT method for relative quantitation, the efficiency of the target and endogenous control must be approximately equal meaning that the assay efficiency should be within 10% of each other, so 100% +/ 10%. If the range is greater than 10%, then you need to be aware that when you evaluate fold changes, the unequal PCR efficiencies will correlate to a decrease in the accuracy of the calculated fold change.
Keep in mind that Life Technologies has well over one million predeveloped Assays, which have been insilico validated to be up to 100% efficient, so the efficiency calculation is not necessary. However, If you do check, and find the efficiency is outside of the acceptable range, then there is likely something from the sample or setup that is throwing things off.
So what happens if my efficiency is say, 150%? Your first thought might be, "Wow, my assay rocks! That's good, right?" Well, actually no. It is not possible to be over 100% efficient, so something else is going on here. Let's review some causes of high or low efficiency, and how to fix them.
First, let's take a look at what's going on with efficiency over 100%. The most common cause of efficiencies greater than 100% are inhibitors. This can be carryover from the sample itself such as heparin or humic acids. Or another source could be contaminants from the RNA or DNA isolation such as SDS or phenol.