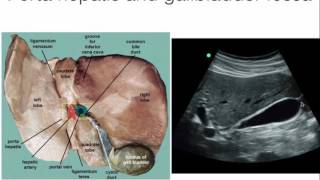
Pediatric Liver Gallbladder u0026 Bile Ducts Ultrasound Normal Vs Abnormal Images | Newborn u0026 Child USG
Pediatric Liver, Gallbladder & Bile Ducts Ultrasound Normal Vs Abnormal Images | Newborn & Child USG
*Cases
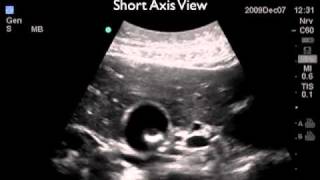
Biliary Atresia 0:00
Choledochal Cyst Type 1 1:34
Gallbladder Ghost Triad 2:00
Hepatic Steatosis (Fatty Liver) 3:22
Liver Cirrhosis 5:05
Cholelithiasis 5:46
Sludge 6:43
Infantile Hepatic Hemangioma 7:30
Focal Infantile Hemangioma 8:20
Multiple Infantile Hemangiomas 8:35
Mesenchymal Hamartoma 9:00
Hepatoblastoma 9:23
Liver Abscess 10:20
Normal Liver Size In Children:
Size (Craniocaudal Length) 03 months: 49 cm approx.
Size (Craniocaudal Length) 36 months: 510 cm approx.
Size (Craniocaudal Length)12.5 years: 711 cm approx.
Size (Craniocaudal Length)35 years: 712 cm approx.
Biliary Atresia: Absence of normal intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts
Neonates present with jaundice 23 weeks after birth
Triangular Cord Sign: Hyperechoic triangular shaped area anterior to portal vein. Measures greater than 4mm. Sign of biliary atresia
Choledochal Cyst Type 1: Cylindrical/Saccular dilation of common bile duct
Anechoic cystic structure at the location of the common bile duct (at the liver hilum)
Gallbladder Ghost Triad: Atretic gallbladder, measuring 1.9cm or less. Irregular or lobular gallbladder contour. Absence of echogenic mucosal layer
Hepatic Steatosis (Fatty Liver): Increased echogenicity of liver parenchyma. Due to cystic fibrosis
Liver Cirrhosis:
Irregular liver surface (Surface nodularity)
Heterogeneous liver appearance
Ascites
Can occur due to biliary atresia, Hepatitis B/C, Wilson’s Disease, Glycogen Storage Diseases, etc.
Cholelithiasis:
Presence of hyperechoic gallstones within the gallbladder
Causes include hemolytic anemia, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, obesity, blood transfusions, etc.
Sludge:
Echogenic thickened mobile bile
No posterior acoustic shadowing
Usually occurs in children receiving total parenteral nutrition
Infantile Hepatic Hemangioma:
Heterogeneous mass
Microcalcifications
Hepatomegaly
Increased vascularity on color doppler
Focal Infantile Hemangioma:
A well defined hyperechoic mass
Multiple Infantile Hemangiomas:
Multiple hypoechoic liver lesions
Mesenchymal Hamartoma:
Multiseptated mass
Multiple cysts
Usually presents in children under 2 years
Hepatoblastoma:
Most common primary malignant tumor in children
Usually presents in children under 4 years
Echogenic/heterogeneous mass
Liver Abscess:
Welldefined mass
Heterogeneous
Peripheral vascularity on color doppler