Pericarditis
ECG Course:
https://www.udemy.com/course/ecgguide
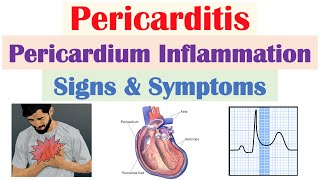
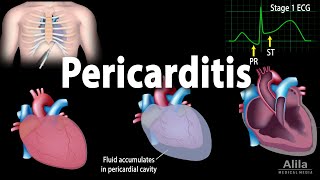
Pericarditis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the pericardium, a doublelayered saclike structure that surrounds the heart and holds it in place within the chest cavity. The pericardium has two layers: the outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer, which produces a small amount of fluid that allows the heart to move smoothly within the pericardial sac.
Pericarditis can be acute, meaning it occurs suddenly and is usually temporary, or chronic, indicating longlasting or recurring inflammation. The condition can result from various causes, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, heart attacks, chest trauma, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or kidney failure. In many cases, the exact cause remains unknown, and this is referred to as idiopathic pericarditis.
*Symptoms:*
*Chest pain:* The most common symptom is sharp, stabbing chest pain behind the breastbone or in the left side of the chest. The pain may worsen when swallowing, coughing, or taking deep breaths and can radiate to the neck, shoulder, or back.
*Fever:* Pericarditis can cause fever, especially if it is due to an infection.
*Shortness of breath:* Inflammation and fluid accumulation around the heart can hinder its normal functioning, leading to breathlessness, especially during physical activity.
*Fatigue:* Patients with pericarditis often feel unusually tired or fatigued.
*Pericardial friction rub:* A healthcare provider can sometimes hear a rubbing or grating sound with a stethoscope, which occurs when the inflamed pericardial layers rub against each other during the heartbeat.
*Diagnosis and Treatment:*
Diagnosis is based on medical history, physical examination, and various tests, including blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), chest Xray, echocardiogram, and sometimes a CT scan or MRI.
Treatment aims to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and treat the underlying cause if identified. Common treatments include:
*Pain relievers:* Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are often used to reduce pain and inflammation.
*Colchicine:* This medication may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrences.
*Corticosteroids:* In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, corticosteroids like prednisone can be used to reduce inflammation.
*Treating underlying cause:* If pericarditis is due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. If it's caused by a viral infection, antiviral medications might be used.
In some cases, especially if there's a significant amount of fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion) or if pericarditis is recurrent, procedures like pericardiocentesis (draining of the fluid) or surgery to remove part or all of the pericardium (pericardiectomy) might be necessary.
It's important for individuals experiencing symptoms of pericarditis, especially chest pain and difficulty breathing, to seek medical attention promptly. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing complications.
Music by INOSSI
Listen: https://bit.ly/3mIA24Z
Watch: • INOSSI Illusion (Official)