Placenta Embryology and Functions
The placenta is a vital organ that develops during pregnancy, playing a crucial role in supporting the growth and development of the fetus. Here's an overview of placenta embryology and its functions:
Placenta Embryology:
Formation:
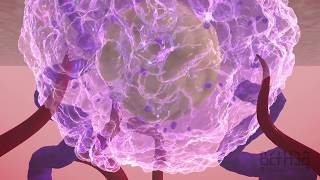
The placenta begins to develop shortly after fertilization. It originates from the outer layer of the blastocyst, called the trophoblast.
The trophoblast differentiates into two layers: the syncytiotrophoblast (outer layer) and the cytotrophoblast (inner layer).
The syncytiotrophoblast invades the uterine lining, establishing a connection between the developing embryo and the mother's blood supply.
Structure
The mature placenta consists of fetal and maternal components. Fetal components include the chorionic plate, chorionic villi, and the umbilical cord.
The maternal side involves the decidua basalis, which is the part of the uterine lining where the placenta attaches.
Blood Supply
Fetal blood vessels within the chorionic villi bring deoxygenated blood close to the maternal blood in the intervillous space.
Exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products occurs across the placental membrane, allowing for the transfer of oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the fetus and removal of waste products from the fetus.
Placenta Functions:
#### 1. *Nutrient and Gas Exchange:*
The primary function of the placenta is to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the maternal and fetal circulations.
Oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood are transported to the fetus, while carbon dioxide and waste products from the fetus are eliminated through the placenta.
#### 2. *Endocrine Functions:*
The placenta produces hormones crucial for maintaining pregnancy, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which sustains the corpus luteum, ensuring a continuous supply of progesterone to support the uterine lining.
It also produces estrogen and progesterone, which help regulate various aspects of pregnancy, including fetal development and maternal adaptations.
#### 3. *Immunological Barrier:*
The placenta acts as a barrier, protecting the fetus from many maternal infections and immune responses.
Immunoglobulins transferred from the mother to the fetus provide passive immunity during the early stages of life.
#### 4. *Waste Elimination:*
Waste products generated by the fetus, such as carbon dioxide and urea, are transported across the placenta and eliminated from the maternal circulation.
#### 5. *Temperature Regulation:*
The placenta helps in maintaining a stable intrauterine environment, assisting in temperature regulation for the developing fetus.
In summary, the placenta is a dynamic organ crucial for the wellbeing of the developing fetus. Its complex structure and functions ensure a supportive and protective environment throughout pregnancy, playing a vital role in the health and development of both the fetus and the mother.
Music by INOSSI
Listen: https://bit.ly/3mIA24Z
Watch: • INOSSI Illusion (Official)