Placenta previa (mechanism of disease)
This is a flowchart on placenta previa, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Risk factors / SDOH
Cell / tissue damage
Structural factors
Placenta previa
Medicine / iatrogenic
Infectious / microbial
Biochem / metabolic
Immunology / inflammation
Signs / symptoms
Tests / imaging / labs
Environmental / toxin
Reproductive physiology
Growth / neoplastic
Pathophysiology
Etiology
Manifestations
Endometrial damage in lower uterine segment
Uterine scarring creates environment that is rich in oxygen and collagen
Implantation of a zygote (fertilized egg) in rich environment
Outer layer of dividing zygote (blastocyst), made of trophoblast cells, develops into placenta
Placenta previa: placenta either partially or completely covers the internal os
Placenta grows toward ↑ blood supply of uterine fundus (while the other side atrophies) → migration
Sudden, painless, bright
red vaginal bleeding
Usually in the third trimester, before rupture of membranes
+/ recurrent bleeding episodes, selflimited; re occurs during onset of labor
Soft, nontender uterus
Usually no fetal distress
Since blood loss is maternal
In contrast to placental abruption
Severe hemorrhage → shock:
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Previous suction
Previous cesarean delivery
Previous / recurrent abortions
Maternal age 35 years
Multiparity
Short interval between pregnancies
Previous placenta previa
Risk factors:
Previous curettage
Assisted reproductive technology
Management:
Lower segment c section is preferred; only attempt vaginal delivery if stable mother, reassuring fetal status, in operating room
In antepartum hemorrhage, avoid digital vaginal exam
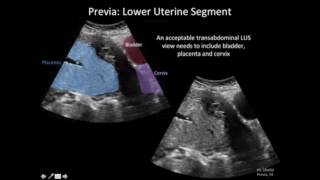
Transvaginal or transabdominal ultrasound, as part of routine prenatal care, assesses placental position