PROPAGATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES _ PART 02
For more information:
http://www.7activestudio.com
[email protected]
http://www.7activemedical.com/
[email protected]
http://www.sciencetuts.com/
[email protected]
Contact: +91 9700061777,
04064501777 / 65864777
7 Active Technology Solutions Pvt.Ltd. is an educational 3D digital content provider for K12. We also customise the content as per your requirement for companies platform providers colleges etc . 7 Active driving force "The Joy of Happy Learning" is what makes difference from other digital content providers. We consider Student needs, Lecturer needs and College needs in designing the 3D & 2D Animated Video Lectures. We are carrying a huge 3D Digital Library ready to use.
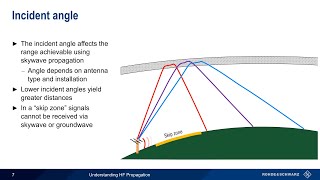
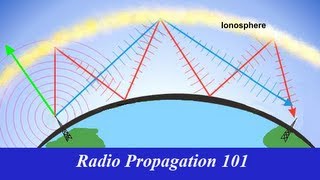
Sky waves:In the frequency range from a few MHz up to 30 to 40 MHz, long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves back towards the earth. This mode of propagation is called sky wave propagation and is used by short wave broadcast services. The ionosphere is so called because of the presence of a large number of ions or charged particles. It extends from a height of ~65 Km to about 400 Km above the earth’s surface. Ionisation occurs due to the absorption of the ultraviolet and other highenergy radiation coming from the sun by air molecules. The ionosphere is further subdivided into several layers, the details of which are given in Table. The degree of ionisation varies with the height. The density of atmosphere decreases with height. At great heights the solar radiation is intense but there are few molecules to be ionised. Close to the earth, even though the molecular concentration is very high, the radiation intensity is low so that the ionisation is again low. However, at some intermediate heights, there occurs a peak of ionisation density. The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for a certain range of frequencies 3 to 30 MHz.Electromagnetic waves of frequencies higher than 30 MHz penetrate the ionosphere and escape. These phenomena are shown in the Figure. The phenomenon of bending of EM waves so that they are diverted towards the earth is similar to total internal reflection in optics. Space wave: Another mode of radio wave propagation is by space waves. A space wave travels in a straight line from transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Space waves are used for lineofsight LOS communication as well as satellite communication. At frequencies above 40 MHz, communication is essentially limited to lineofsight paths. At these frequencies, the antennas are relatively smaller and can be placed at heights of many wavelengths above the ground. Because of lineofsight nature of propagation, direct waves get blocked at some point by the curvature of the earth as illustrated in Figure. If the signal is to be received beyond the horizon then the receiving antenna must be high enough to intercept the lineofsight waves.If the transmitting antenna is at a height hT, then you can show that the distance to the to the horizon dT is give where R is the radius of the earth approximately 6400 km.