Secrets of Catalase Unveiled: What Happens When pH Levels Go Extreme?
Receive Comprehensive Mathematics Practice Papers Weekly for FREE
Click this link to get: ▶▶▶ https://iitutor.com/emaillist/ ◀◀◀
Unlock the astonishing secrets of Catalase in this mindboggling exploration of extreme pH levels! Catalase, a remarkable enzyme found in all oxygenbreathing organisms, holds the key to dismantling hydrogen peroxide, a potentially toxic byproduct, into harmless water and oxygen. But what happens when pH levels go off the charts?
Join us on this scientific journey as we push Catalase to its limits. You'll discover why pH 4 sends it into hiding, while pH 10 challenges its resilience.
Our hypothesis? When this enzyme meets pH extremes beyond its comfort zone, denaturation becomes its destiny. Will our experiment support this theory? The results are nothing short of astonishing!
So, grab your lab coat and your inquisitive mind, and let's dive into the captivating world of Catalase and pH. Science has never been this eyeopening! Happy learning!
Unlock the astonishing secrets of Catalase in this mindboggling exploration of extreme pH levels! Catalase, a remarkable enzyme found in all oxygenbreathing organisms, holds the key to dismantling hydrogen peroxide, a potentially toxic byproduct, into harmless water and oxygen. But what happens when pH levels go off the charts?
Join us on this scientific journey as we push Catalase to its limits. You'll discover why pH 4 sends it into hiding, while pH 10 challenges its resilience.
Our hypothesis? When this enzyme meets pH extremes beyond its comfort zone, denaturation becomes its destiny. Will our experiment support this theory? The results are nothing short of astonishing!
So, grab your lab coat and your inquisitive mind, and let's dive into the captivating world of Catalase and pH. Science has never been this eyeopening! Happy learning!
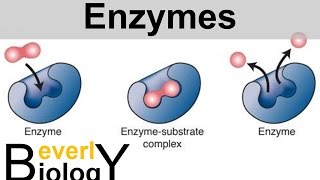
Catalase is an enzyme found in all organisms that breathe oxygen. This enzyme facilitates the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (a toxic byproduct of the body) into water and oxygen. Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one molecule of catalase can convert 40 million molecules of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen each second. Hydrogen peroxide must be quickly converted into other, less dangerous substances to prevent damage to cells and tissues.
Catalase is an enzyme that rapidly catalyses the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into less reactive substances; gaseous oxygen and water molecules. The optimum pH for human catalase is approximately 7 and has a fairly broad maximum (the rate of reaction does not change appreciably at pHs between 6.8 and 7.5). Sources of catalase include; sliced raw potato, ground meat, liver. Hypothesis: When catalase (enzyme) is added to a medium higher or lower pH outside its optimal pH range, the enzyme will denature and, therefore not convert hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
1. Place catalase paper in pH 4.
2. Using a stopwatch, determine how long it takes for the reaction to take place.
3. Repeat steps 12 with catalase in solutions of pH 7 and pH 10.
4. Record results in a table and draw a graph. pH 4 – There was no reaction; the enzyme has denatured. pH 7 – Fastest reaction at 90 seconds to complete. pH 10 – Slowest reaction at 5 minutes to complete.
What do the results show? Did your results support your hypothesis? Are your results valid? Could this experiment be improved? Name any safety precautions you followed. Because pH 10 still achieved a reaction, the enzyme did perform at this pH level. The enzyme may be able to withstand varying pH levels. However, it performs best at pH 7 and doesn’t perform at all at pH 4.