Sextant to Line of Position - A Complete Sight Reduction from an Offshore Sailing Race
I recently returned from a sailing race and along the way I took some Sun Sights using a sextant with my friend Chuck. In this video, we will reduce one of the sights from beginning to end. We'll cover all the celestial navigation theory and math required to take a sextant reading to a usable line of position on a chart.
The five main steps are:
1: Observe and correct the sight.
2. Find the geographic position of the sun.
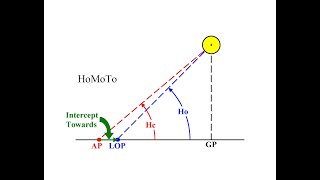
3. Build a spherical triangle.
4. Solve that triangle using formulas or HO229.
5. Compare the computed value to the observed value and plot it.
This sight reduction uses the St. Hilaire method of altitude/intercept. It also relies on the Nautical Almanac and HO229, both of which are available for download from the internet for free.
Nautical Almanac and HO229 available here https://www.thenauticalalmanac.com/
For more on celestial navigation, you can refer to other videos on this channel, specifically the 11part celestial navigation series from 2013 (starting with Getting Starting in Celestial Navigation).
• Celestial Navigation (All Films)
For free and discount marine navigation courses, visit www.practicalnavigator.org. Thank you for your support!
Time Stamps:
0:00 Introduction
0:46 General Navigation Background
5:23 Using the Sun as a Lighthouse in the Sky
7:10 Geographic Position on a Curved Earth
10:07 Celestial Navigation Theory Circles of Position
13:30 Step 1: Observe and Correct the Sight
29:05 Step 2: Find the Geographic Position of the Sun
39:46 Step 3: Build a Spherical Triangle
49:14 Step 4: Solve the Triangle
53:57 Step4A: Direct Mathematics Solution
55:25 Step 4B: HO229 Solution
1:01:34 Step 5 Compare and Plot the Solution
1:11:29 Review and Conclusion