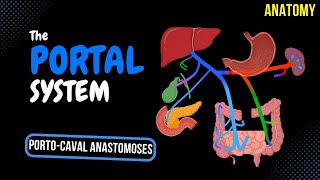
Superior and Inferior Mesenteric Veins | Venous Drainage of small intestine
INFERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN
The inferior mesenteric vein is a large venous trunk located in the abdomen. It is a continuation of the superior anorectal vein, also referred to as the superior rectal vein. The inferior mesenteric vein is located in the retroperitoneum, coursing superiorly and towards the left side, while being accompanied by the inferior mesenteric artery.
The main function of the inferior mesenteric vein is to drain blood from the hindgut, a portion of the gastrointestinal tract that includes the structures from the distal transverse colon to the rectum.
Origin and course
Inferior mesenteric vein (Vena mesenterica inferior); Image: Begoña Rodriguez
Inferior mesenteric vein (Vena mesenterica inferior)
The inferior mesenteric vein arises in the lower abdomen as a continuation of the superior rectal vein that drains the rectal (hemorrhoidal) venous plexus. The inferior mesenteric vein runs retroperitoneally, ascending from its origin to the left side. Along its course, it crosses the left psoas major muscle, the left ureter and left gonadal (testicular/ovarian) vessels. Upon reaching the left side of the duodenojejunal flexure, the inferior mesenteric vein curves to the right and passes posterior to the body of the pancreas. Here, it terminates by draining into the splenic vein, which then merges with the superior mesenteric vein to form the hepatic portal vein. Occasionally, the inferior mesenteric vein may drain into the superior mesenteric vein instead, or into its confluence with the splenic vein.
Tributaries and drainage area
Sigmoid veins (Venae sigmoideae); Image: Begoña Rodriguez
Sigmoid veins (Venae sigmoideae)
Along its relatively long course across the abdominal cavity, the inferior mesenteric vein receives the sigmoid and left colic veins as tributaries. Thereby, the inferior splenic vein drains blood from the rectum, sigmoid, descending and distal transverse colon. Together, the superior and inferior mesenteric veins drain the majority of the gastrointestinal tract, from the stomach to the rectum.
Explore our articles, quizzes, video tutorials and labeled diagrams to learn everything about the blood vessels of the rectum.
SUPERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN
The superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a large venous vessel located in the abdomen. It arises within the mesentery of the small intestine from the small tributaries that drain blood from the terminal ileum, caecum and vermiform appendix. It terminates by uniting with the splenic vein and forming the portal vein.
The main function of the superior mesenteric vein is to drain the blood from the distal portion of the gastrointestinal tract. Specifically, it drains the small intestine, caecum, ascending and transverse parts of the colon, and distal parts of the stomach and greater omentum.
Origin and course
Superior mesenteric vein (Vena mesenterica superior); Image: Begoña Rodriguez
Superior mesenteric vein (Vena mesenterica superior)
The superior mesenteric vein is a large abdominal vein that is formed by the small terminal veins that drain the ileum, caecum and vermiform appendix. It runs superomedially, traversing the mesentery of the small intestine. Along its course, the vein accompanies the superior mesenteric artery that runs on its left side.
The superior mesenteric vein terminates at the transpyloric plane (around the lower margin of the L1 vertebra) by merging with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein.
Tributaries and drainage area
Jejunal veins (Venae jejunales); Image: Irina Münstermann
Jejunal veins (Venae jejunales)
The superior mesenteric vein has numerous tributaries that drain the structures of the gastrointestinal tract, starting from the distal stomach to the transverse colon. These tributaries are:
The jejunal vein
The ileal vein
The ileocolic vein
The right colic vein
The middle colic vein
The right gastroepiploic vein
The inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein
By collecting the blood from these veins, the superior mesenteric vein carries the nutrients absorbed in the small intestine into the hepatic portal vein. The portal vein then conveys them to the liver, which then metabolically processes those nutrients and prepares them to be distributed throughout the body.
Explore our articles, quizzes, video tutorials and labeled diagrams to learn everything about the veins of the small intestine.