Syphilis (mechanism of disease)
This is a flowchart on syphilis, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations, including that for the JarischHerxheimer reaction.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Risk factors / SDOH
Cell / tissue damage
Structural factors
Syphilis
Medicine / iatrogenic
Infectious / microbial
Biochem / metabolic
Immunology / inflammation
Signs / symptoms
Tests / imaging / labs
Environmental, toxin
Neurology pathology
Flow physiology
Pathophysiology
Etiology
Manifestations
Treponema pallidum: gramneg; spiralshaped bacteria; spirochete family
Sexual contact (via small mucocutaneous lesions) during direct vaginal, anal, oral contact
Transmission via …
Vertical (from mother to child) during pregnancy or birth
Blood transfusion or organ donations (rare)
Spirochetes disseminate systematically via the lymphatic system and the bloodstream within hours
Treponema bacteria is highly contagious during stages I and II
Treponemes cause obliterating endarteritis at entry site
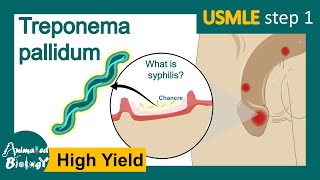
Primary syphilis:
Primary lesion (chancre):
Typically starts out as a solitary, raised papule,usually on the genitals (9095%) → painless, firm ulcer with indurated borders and smooth base → resolves spontaneously within 36 weeks without scarring
Ischemic death of sensory vasa nervorum
Nontender regional lymphadenopathy
Painless
Inflammatory reaction: endarteritis (+/ obliterating → ischemia, necrosis) and perivascular inflammatory infiltrates (type IV hypersen.)
Nontender regional lymphadenopathy
Fever, fatigue, myalgia, headache
Polymorphic rash: typically disseminated, nonpruritic macular or papular rash; involves trunk, extremities, palms, soles; reddishbrown or coppercolored; heals within 6 months; +/ recurrence
Condylomata lata: broadbased, wartlike, smooth, white papular erosions; painless; located in anogenital regions, intertriginous folds, on oral mucosa
Secondary syphilis:
Latent syphilis: seropositive but no clinical symptoms; can last months, years, or for life
Aortitis, syphilitic mesaortitis
Gumma: destructive lesions with necrotic center; tends to ulcerate; affects any organ
Tertiary syphilis:
Gumma in CNS is neurosyphilis:
Treponemainduced vasculitis of vasa vasorum of large vessels
Vessel wall atrophy
Ascending aortic aneurysm (thoracic aortic aneurysm); aortic root dilation and insufficiency
Perivascular inflammatory infiltrate that consists mainly of monocytes → destructive granulomas
Immunosuppression
Coinfection with HIV
Acute meningeal syphilis: symptoms of acute meningitis (but aseptic) → neck stiffness, nausea
Meningovascular syphilis: subacute stroke, cranial neuropathies
Argyll Robertson pupil: bilateral miosis; pupils accommodate but do not react to direct or indirect light
Tabes dorsalis: demyelination of dorsal columns and DRG: impaired proprioception → progressive sensory broadbased ataxia (+ Romberg); absent deep tendon reflexes; loss of sensation in the lower extremities; sharp, shooting pain in the legs and the abdomen; Charcot joint
Most often seen if treatment begins in the early phases of the secondary stage
Acute, transient, systemic reaction to bacterial endotoxinlike substances and pyrogens that are released after initiation of antibiotic therapy
JarischHerxheimer reaction:
Antibiotics
Flulike: fever, chills, headache, myalgia
Tachypnea, hypotension, tachycardia
Selflimiting within 12–24 hours













![Serologic Testing for Syphilis [Hot Topic]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/iG82umIwC3Q/mqdefault.jpg)












