Tibial Nerve Anatomy Animation : Origin course Branches Tarsal tunnel syndrome | USMLE Step 1
: / drgbhanuprakash
: https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr
: https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Tibial Nerve Anatomy Animation : Origin, course, Branches, Tarsal tunnel syndrome | USMLE Step 1
The tibial nerve is one of the two major branches of the sciatic nerve, the other being the common peroneal nerve (or common fibular nerve). Here's a detailed look at its anatomy:
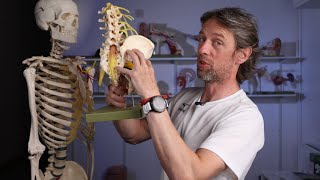
Origin: The tibial nerve originates in the sacral plexus. It is formed from the anterior divisions of the L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3 nerve roots.
Course: The tibial nerve descends from its origin, travels through the buttock region, and down the posterior aspect of the thigh. It then continues through the popliteal fossa, where it gives off several branches before continuing down the calf and into the foot.
Branches:
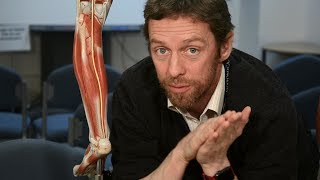
Muscular branches: These branches supply the hamstring muscles (except the short head of the biceps femoris, which is innervated by the common peroneal nerve) and some muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg (the gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus).
Cutaneous branches: The sural nerve, a cutaneous branch, provides sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior and lateral aspect of the lower leg and the lateral side of the foot.
Articular branches: These branches supply the hip and knee joints.
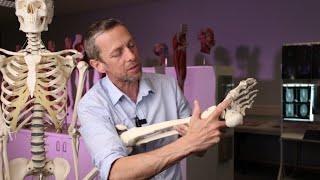
The tibial nerve continues into the foot by passing behind the medial malleolus in the tarsal tunnel, where it branches into the medial and lateral plantar nerves.
Innervation: The tibial nerve provides motor innervation to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar aspect of the foot. It provides sensory innervation to the skin on the sole of the foot.
Clinical Anatomy:
Damage or compression of the tibial nerve can cause various clinical conditions, including:
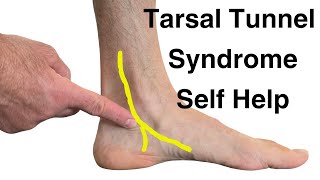
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: This occurs when the tibial nerve is compressed as it passes under the flexor retinaculum in the foot, leading to pain and numbness in the sole of the foot.
Sciatica: Irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve or its roots can cause pain that radiates down the leg along the path of the sciatic nerve and its branches, including the tibial nerve.
For the USMLE, it's essential to understand the tibial nerve's anatomy, branches, and the areas it innervates, as well as the clinical implications of injury or disease involving this nerve.
#TibialNerve #Anatomy #Neuroanatomy #SciaticNerve #NerveInnervation #ClinicalAnatomy #USMLE #MedicalStudies #MedicalExam #tibialNerveBranches #tibialNerveCourse #tibialNerveOrigin #fmge #fmgevideos #rapidrevisionfmge #fmgejan2023 #mbbslectures #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #neetpg #usmlepreparation #usmlestep1 #fmge #usmle #drgbhanuprakash #medicalstudents #medicalstudent #medicalcollege #neetpg2023 #usmleprep #usmlevideos #usmlestep1videos #medicalstudents #neetpgvideos #tarsaltunnelsyndrome