Tietze syndrome
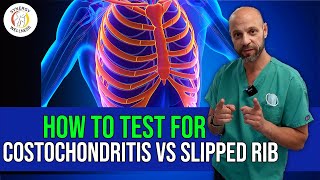
A benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages, characterized by tenderness and painful swelling of the anterior chest wall at the costochondral (ribcartilage), sternocostal (cartilagesternum), or sternoclavicular (claviclesternum) junctions. It affects the true ribs (especially, the 2nd3rd), commonly only a single joint.
The most common symptom is pain, primarily in the chest, but can also radiate to the shoulder and arm.
Symptoms can be both sudden and gradual, and the pain and swelling are typically chronic and intermittent and can last from a few days to several weeks.
They can be exacerbated by sneezing, coughing, deep inhalation, and overall physical exertion.
Many patients begin developing symptoms following a respiratory infection and dry cough, therefore, microtrauma (small tears in the ligament) is hypothesized to be the cause. However, the exact cause is not known.
In the emergency room, despite a musculoskeletal condition, it can be misdiagnosed as lifethreatening cardiopulmonary conditions, such as, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, pleurisy, due to chest pain.
However, it should be ruled out prior to diagnosis of other conditions.
(Differential diagnosis)
• Tietze syndrome: Affects the 2nd or 3rd rib. Present with swelling of the costal cartilages, radiating pain to the shoulder and arm. Diagnosed by ultrasound.
• costochondritis: Affects the 2nd to 5th ribs. Not present with heat, erythema, or swelling of the affected area. Diagnosed by physical examination (e.g. crowing rooster maneuver).
• slipping rib syndrome: Affects the 1st to 7th ribs (true ribs) and 8th to 10th ribs (false ribs). Characterized by the subluxation (partial dislocation) of the joints between the costal cartilages, radiating pain to the shoulder and arm. It can also cause abdominal and back pain. Diagnosed by physical examination (e.g. hooking maneuver) and dynamic ultrasound.
• serious cardiopulmonary conditions: E.g. myocardial infarction,angina pectoris, aortic dissection. Diagnosed by physical examination (e.g. reproducible chest wall tenderness) and an electrocardiogram.
• pleural diseases: E.g. pleurisy, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax.
• rheumatic disorders: E.g. arthritis of the costal cartilages, ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatic fever.
• neoplasms: E.g. chondroma, osteochondroma, multiple myeloma, osteosarcoma, Hodgkin lymphoma.
• nerve pain: Specifically intercostal neuritis and intercostal neuropathy.
(Treatment)
• rest: It is considered to be a selflimiting condition.
• pain management
manual therapy
local heat application
nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
analgesics
• intercostal nerve block: Uses nerveblocking injection that consists of a combination of steroids (e.g. hydrocortisone, triamcinolone hexacetonide) and anesthetics (e.g. lidocaine, procaine), which is typically administered under ultrasound guidance.
• surgery: The resection of the affected costal cartilages and some of the surrounding areas. Only for refractory cases, resistant to other conservative treatment options (severe, chronic forms).