Torsion Equation Importance || Torsion Equation पढ़ना ही कियु है
#sscje #mechanical #gearinstitute
Click here to download our app
https://edumartin.page.link/jLFr
Join telegram channel
https://t.me/gearinstitute
JE की तयारी के लिए App Download करें
https://edumartin.page.link/jLFr
Join our whats app channel
https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaCP...
ALL IN 1 AE/JE EXAM LIVE CLASSES (TECHNICAL +NON TECHNICAL)
https://bit.ly/452qVRR
ALL IN 1 AE/JE EXAM LIVE CLASSES (TECHNICAL ONLY)
https://bit.ly/3Rp4ykf
SSC JE RECORDED COURSE (2YEAR VALIDITY).
http://bit.ly/3CSOuzH
SSC JE RECORDED COURSE (1YEAR VALDITY)
http://bit.ly/3W9LVjv
Mechanical MCQ Book written by Er.Harvinder Singh
Order your copy click here
https://bit.ly/MCQBOOK
TORSION
Learning Objectives
At the end of this chapter you should be able to complete torsion calculations using:
General torsion equation
Polar moment of inertia
Modulus of elasticity in shear
Shafts are mechanical components, usually of circular crosssection, used to transmit power/torque through their rotational motion. In operation they are subjected to:
torsional shear stresses within the crosssection of the shaft, with a maximum at the outer surface of the shaft
bending stresses (for example a transmission gear shaft supported in bearings)
vibrations due to critical speeds
This chapter will focus exclusively on evaluating shear stresses in a shaft.
General torsion equation
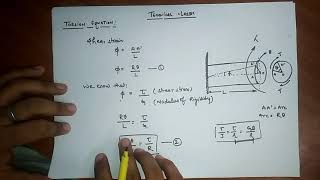
All torsion problems that you are expected to answer can be solved using the following formula:
where:
T = torque or twisting moment, [N×m, lb×in]
J = polar moment of inertia or polar second moment of area about shaft axis, [m4, in4]
τ = shear stress at outer fibre, [Pa, psi]
r = radius of the shaft, [m, in]
G = modulus of rigidity (PanGlobal and Reed’s) or shear modulus (everybody else), [Pa, psi]
θ = angle of twist, [rad]
L = length of the shaft, [m, in]
The nomenclature above follows the same convention as PanGlobal Power Engineering Training System.
Most common torsion problems will indicate the transmitted power (kW) at a certain rotational speed (rad/s or RPM). The equivalent torque can be found with:
where n[rad/s] = N[rev/min]×2π/60.
Polar moment of inertia
Similar to the moments of inertia that you learned before in rotational kinetics and bending of beams, the polar moment of inertia represents a resistance to twisting deformation in the shaft. General formulas for polar moment of inertia are given in Textbook Appendix C.
Note the difference between bending moments of inertia Ic and polar moments of inertia J, and use them appropriately. For instance, if you are dealing with a circular bar:
Ic = π d4 / 64, if the bar is used as a beam
J = π d4 / 32, if the bar is used as a shaft
Shear modulus
Called Modulus of Rigidity in PanGlobal and Reed’s, the shear modulus is defined (similarly as E) as ratio of shear stress to the shear strain. It is expressed in GPa or psi and typical values are given in Textbook Appendix B. Typical values are lower than Young’s Modulus E, for instance ASTM A36 steel has EA36 = 207 GPa and GA36 = 83 GPa.
Angle of twist
The torque deformation of a shaft due is measured by the twist angle at the end of the shaft. This angle of twist depends on the length of the shaft, as shown in the following figure:
by Barry Dupen [1]
The angle of twist, [radians] is used in the general torsion equation and in estimating the shear strain, γ (gamma), nondimensional.
Torsion Equation
Torsion Equation in hindi
Torsion Equation derivation
Torsion Equation derivation in hindi
Torsion Equation derive
derive Torsion Equation
torsion formula derivation
derive torsion formula
Torsion equation for hollow and solid shaft
torsion equation for solid shaft
torsion equation for circular shaft
Torsion equation kya hoti hai
Torsional Equation (हिन्दी )
Torsion Equation | Torsion in circular shaft | Derivation | Hindi
Bending equation in hindi || Torsion equation in hindi || trick to remember bending and torsion eqn
Strength of Materials | Module 5 | TORSION EQUATION | (Lecture 49)
T = torque
r = radius
F = force
theta = angle between F and the lever arm
From the web
General torsion equation
T = torque or twisting moment, [N×m, lb×in] J = polar moment of inertia or polar second moment of area about shaft axis, [m4, in4] τ = shear stress at outer fibre, [Pa, psi] r = radius of the shaft, [m, in]
torsion equation,torsion equation derivation,torsion formula,torsion equation for solid and hollow circular shaft,torsion equation derivation in hindi,torsion equation derivation pdf,torsion equation in hindi,torsion equation in strength of materials,torsion equation in som









![The most beautiful equation in math, explained visually [Euler’s Formula]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/f8CXG7dS-D0/mqdefault.jpg)


















