Urine Analysis for Abnormal Constituent | Sugar Test by Benedict's Reagent in Urine | यूरिन सुगर
Also available in ENGLISH. Determination of Sugar in Urine = Benedict Test (Pathology Experiment)= ENGLISH By Solution Pharmacy • Determination of Sugar in Urine | Ben...
Download "Solution Pharmacy" Mobile App to Get All Uploaded Notes, Model Question Papers, Answer Papers, Online Test and other GPAT Materials https://play.google.com/store/apps/de...
Basic Cause and reason for Diabetes • Diabetes Mellitus | Cause Symptoms Ty...
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which blood sugar (glucose) levels are abnormally high because the body does not produce enough insulin to meet its needs.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
In type 1 diabetes (formerly called insulindependent diabetes or juvenileonset diabetes), the body's immune system attacks the insulinproducing cells of the pancreas, and more than 90% of them are permanently destroyed. The pancreas, therefore, produces little or no insulin. Only about 5 to 10% of all people with diabetes have type 1 disease. Most people who have type 1 diabetes develop the disease before age 30, although it can develop later in life.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
In type 2 diabetes (formerly called non– insulindependent diabetes or adultonset diabetes), the pancreas often continues to produce insulin, sometimes even at higherthannormal levels, especially early in the disease. However, the body develops resistance to the effects of insulin, so there is not enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. As type 2 diabetes progresses, the insulinproducing ability of the pancreas decreases.
Complications of diabetes
(1) Brain, causing a stroke
(2) Eyes (diabetic retinopathy), causing blindness
(3) Heart, causing a heart attack
(4) Kidneys (diabetic nephropathy), causing chronic kidney disease
(5) Nerves (diabetic neuropathy), causing a decreased sensation in feet
Benedict’s solution is a deepblue alkaline chemical reagent used to test for the presence of the aldehyde functional group CHO which consists of copper sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4. 5H2O), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7) and distilled water. Sodium carbonate renders alkaline conditions which are required for the redox reaction, while sodium citrate is a complexing agent which complexes with the copper (II) ions to avoid degradation into copper (I) ions during storage.
Principle of Benedicts test
Benedict’s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar solution with Benedict‘s reagent. The presence of the alkaline sodium carbonate converts the sugar into a strong reducing agent called enediols. During the reaction, enediols decrease the cupric particles (Cu2+) present in Benedict’s reagent to cuprous particles (Cu+) which appear as red copper oxide (Cu2O) which is insoluble in water. When Benedict’s reagent solution and reducing sugars are heated together, the solution changes its color to orangered/ brick red precipitate. The redcolored cuprous oxide is insoluble in water and hence, separate out from the solution. When the concentration of the reducing sugar is high in the solution, then the color becomes more intense (reddish) and the volume of the precipitate increases in the test tube making it clearly visible.
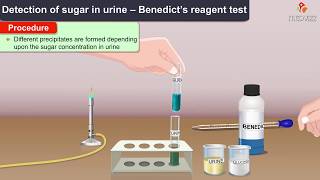
The procedure of Benedict’s Test
1. Pipette out 2 ml (10 drops) of Benedict’s reagent and placed it in the clean test tube
2. Approximately 1 ml of sample (urine) is added to Benedict’s reagent.
3. The test tube is placed over the boiling water bath for 35 minutes (can be heated directly over flame).
4. Observe for color change in the solution of test tubes or precipitate formation.
Result Interpretation of Benedict’s Test
1. If the color upon boiling is changed into green, then there would be 0.1 to 0.5 percent sugar in solution.
2. If it changes color to yellow, then 0.5 to 1 percent sugar is present.
3. If it changes to orange, then it means that 1 to 1.5 percent sugar is present.
4. If color changes to red,then 1.5 to 2.0 percent sugar is present.
5. And if color changes to brick red,it means that more than 2 percent sugar is present in solution.
Get in touch with the solution by just clicking the following links
Facebook Group / solutionpharamcy
Facebook Page / pharmavideo
New Channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) / @pharmacydictionary
Instagram / solutionpharmacy
EMail for official and other work [email protected]
LinkedIn / pushpendrakpatel
#solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #Pharmacognosyvideos #GPATonlinetest #GPATclass #GPATvideos #Microbiologyclass#Microbiology#